 |
PDBsum entry 4j6e
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structure of lpxi d225a mutant
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Udp-2,3-diacylglucosamine pyrophosphatase lpxi. Chain: a. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Caulobacter crescentus. Organism_taxid: 565050. Strain: cb15n. Gene: 77330127, ccna_01987, cc_1910, lpxi. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.52Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.227
|
R-free:
|
0.286
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
L.E.Metzger Iv,J.K.Lee,J.S.Finer-Moore,C.R.H.Raetz,R.M.Stroud,Center For Structures Of Membrane Proteins (Csmp)
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
L.E.Metzger
et al.
(2012).
LpxI structures reveal how a lipid A precursor is synthesized.
Nat Struct Biol,
19,
1132-1138.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
11-Feb-13
|
Release date:
|
08-May-13
|
|
|
Supersedes:
|

|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
A0A0H3C8Q1
(A0A0H3C8Q1_CAUVN) -
UDP-2,3-diacylglucosamine pyrophosphatase LpxI from Caulobacter vibrioides (strain NA1000 / CB15N)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
280 a.a.
273 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.6.1.54
- UDP-2,3-diacylglucosamine diphosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a UDP-2-N,3-O-bis[(3R)-3-hydroxyacyl]-alpha-D-glucosamine + H2O = a lipid X + UMP + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
UDP-2-N,3-O-bis[(3R)-3-hydroxyacyl]-alpha-D-glucosamine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
lipid X
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 70.59% similarity
|
+
|
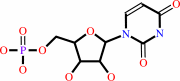 UMP
UMP
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Nat Struct Biol
19:1132-1138
(2012)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
LpxI structures reveal how a lipid A precursor is synthesized.
|
|
L.E.Metzger,
J.K.Lee,
J.S.Finer-Moore,
C.R.Raetz,
R.M.Stroud.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Enzymes in lipid metabolism acquire and deliver hydrophobic substrates and
products from within lipid bilayers. The structure at 2.55 Å of one isozyme of
a constitutive enzyme in lipid A biosynthesis, LpxI from Caulobacter crescentus,
has a novel fold. Two domains close around a completely sequestered substrate,
UDP-2,3-diacylglucosamine, and open to release products either to the
neighboring enzyme in a putative multienzyme complex or to the bilayer. Mutation
analysis identifies Asp225 as key to Mg(2+)-catalyzed diphosphate hydrolysis.
These structures provide snapshots of the enzymatic synthesis of a critical
lipid A precursor.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

