 |
PDBsum entry 4drh

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Isomerase/transferase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4drh
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Isomerase/transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Co-crystal structure of the ppiase domain of fkbp51, rapamycin and the frb fragment of mtor at low ph
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase fkbp5. Chain: a, d. Fragment: fkbp51 fk1 domain, unp residues 1-140. Synonym: ppiase fkbp5, 51 kda fk506-binding protein, 51 kda fkbp, fkbp-51, 54 kda progesterone receptor-associated immunophilin, androgen-regulated protein 6, ff1 antigen, fk506-binding protein 5, fkbp-5, fkbp54, p54, hsp90-binding immunophilin, rotamase. Engineered: yes. Serine/threonine-protein kinase mtor.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: aig6, fkbp5, fkbp51. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008. Gene: frap, frap1, frap2, mtor, raft1, rapt1.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.30Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.189
|
R-free:
|
0.226
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.M.Maerz,A.Bracher,F.Hausch
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
A.M.März
et al.
(2013).
Large FK506-binding proteins shape the pharmacology of rapamycin.
Mol Cell Biol,
33,
1357-1367.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
17-Feb-12
|
Release date:
|
06-Feb-13
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q13451
(FKBP5_HUMAN) -
Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP5 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
457 a.a.
132 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, D:
E.C.5.2.1.8
- peptidylprolyl isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[protein]-peptidylproline (omega=180) = [protein]-peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
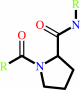 Peptidylproline (omega=180)
Peptidylproline (omega=180)
|
=
|
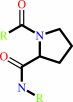 peptidylproline (omega=0)
peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains B, E:
E.C.2.7.10.2
- non-specific protein-tyrosine kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-tyrosyl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-tyrosyl-[protein] + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-tyrosyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
O-phospho-L-tyrosyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
Chains B, E:
E.C.2.7.11.1
- non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
L-seryl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-seryl-[protein] + ADP + H+
|
|
2.
|
L-threonyl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein] + ADP + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-seryl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
O-phospho-L-seryl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-threonyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Mol Cell Biol
33:1357-1367
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Large FK506-binding proteins shape the pharmacology of rapamycin.
|
|
A.M.März,
A.K.Fabian,
C.Kozany,
A.Bracher,
F.Hausch.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The immunosuppressant and anticancer drug rapamycin works by inducing inhibitory
protein complexes with the kinase mTOR, an important regulator of growth and
proliferation. The obligatory accessory partner of rapamycin is believed to be
FK506-binding protein 12 (FKBP12). Here we show that rapamycin complexes of
larger FKBP family members can tightly bind to mTOR and potently inhibit its
kinase activity. Cocrystal structures with FKBP51 and FKBP52 reveal the modified
molecular binding mode of these alternative ternary complexes in detail. In
cellular model systems, FKBP12 can be functionally replaced by larger FKBPs.
When the rapamycin dosage is limiting, mTOR inhibition of S6K phosphorylation
can be enhanced by FKBP51 overexpression in mammalian cells, whereas FKBP12 is
dispensable. FKBP51 could also enable the rapamycin-induced hyperphosphorylation
of Akt, which depended on higher FKBP levels than rapamycin-induced inhibition
of S6K phosphorylation. These insights provide a mechanistic rationale for
preferential mTOR inhibition in specific cell or tissue types by engaging
specific FKBP homologs.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| |

