 |
PDBsum entry 4d12

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4d12
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.7.3.3
- factor independent urate hydroxylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
AMP Catabolism
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
urate + O2 + H2O = 5-hydroxyisourate + H2O2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
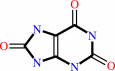 urate
urate
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
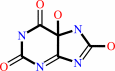 5-hydroxyisourate
5-hydroxyisourate
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Copper
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl
53:13710-13714
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Direct evidence for a peroxide intermediate and a reactive enzyme-substrate-dioxygen configuration in a cofactor-free oxidase.
|
|
S.Bui,
D.von Stetten,
P.G.Jambrina,
T.Prangé,
N.Colloc'h,
D.de Sanctis,
A.Royant,
E.Rosta,
R.A.Steiner.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Cofactor-free oxidases and oxygenases promote and control the reactivity of O2
with limited chemical tools at their disposal. Their mechanism of action is not
completely understood and structural information is not available for any of the
reaction intermediates. Near-atomic resolution crystallography supported by
in crystallo Raman spectroscopy and QM/MM calculations showed unambiguously
that the archetypical cofactor-free uricase catalyzes uric acid degradation via
a C5(S)-(hydro)peroxide intermediate. Low X-ray doses break specifically the
intermediate C5OO(H) bond at 100 K, thus releasing O2 in situ, which is
trapped above the substrate radical. The dose-dependent rate of bond rupture
followed by combined crystallographic and Raman analysis indicates that ionizing
radiation kick-starts both peroxide decomposition and its regeneration.
Peroxidation can be explained by a mechanism in which the substrate radical
recombines with superoxide transiently produced in the active site.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

