 |
PDBsum entry 4c6t

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Immune system
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4c6t
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Immune system
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of the rps4 and rrs1 tir domain heterodimer
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Probable wrky transcription factor 52. Chain: a, c. Fragment: toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain, residues 6-153. Synonym: disease resistance protein rrs1, disease resistance protein slh1, protein sensitive to low humidity 1, resistance to ralstoni a solanacearum 1 protein, wrky DNA-binding protein 52. Engineered: yes. Disease resistance protein rps4. Chain: b, d.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Arabidopsis thaliana. Organism_taxid: 3702. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008. Expression_system_variant: rosetta.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.65Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.185
|
R-free:
|
0.227
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.J.Williams,K.H.Sohn,L.Wan,M.Bernoux,Y.Ma,C.Segonzac,T.Ve,P.Sarris, D.J.Ericsson,S.B.Saucet,X.Zhang,J.Parker,P.N.Dodds,J.D.G.Jones, B.Kobe
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
S.J.Williams
et al.
(2014).
Structural basis for assembly and function of a heterodimeric plant immune receptor.
Science,
344,
299-303.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
19-Sep-13
|
Release date:
|
28-May-14
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains B, D:
E.C.3.2.2.6
- ADP-ribosyl cyclase/cyclic ADP-ribose hydrolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
NAD+ + H2O = ADP-D-ribose + nicotinamide + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
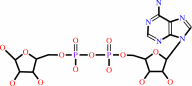 ADP-D-ribose
ADP-D-ribose
|
+
|
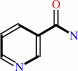 nicotinamide
nicotinamide
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Science
344:299-303
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis for assembly and function of a heterodimeric plant immune receptor.
|
|
S.J.Williams,
K.H.Sohn,
L.Wan,
M.Bernoux,
P.F.Sarris,
C.Segonzac,
T.Ve,
Y.Ma,
S.B.Saucet,
D.J.Ericsson,
L.W.Casey,
T.Lonhienne,
D.J.Winzor,
X.Zhang,
A.Coerdt,
J.E.Parker,
P.N.Dodds,
B.Kobe,
J.D.Jones.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Cytoplasmic plant immune receptors recognize specific pathogen effector proteins
and initiate effector-triggered immunity. In Arabidopsis, the immune receptors
RPS4 and RRS1 are both required to activate defense to three different
pathogens. We show that RPS4 and RRS1 physically associate. Crystal structures
of the N-terminal Toll-interleukin-1 receptor/resistance (TIR) domains of RPS4
and RRS1, individually and as a heterodimeric complex (respectively at 2.05,
1.75, and 2.65 angstrom resolution), reveal a conserved TIR/TIR interaction
interface. We show that TIR domain heterodimerization is required to form a
functional RRS1/RPS4 effector recognition complex. The RPS4 TIR domain activates
effector-independent defense, which is inhibited by the RRS1 TIR domain through
the heterodimerization interface. Thus, RPS4 and RRS1 function as a receptor
complex in which the two components play distinct roles in recognition and
signaling.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

