 |
PDBsum entry 4c6c
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.2.1.3.2
- aspartate carbamoyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Pyrimidine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
carbamoyl phosphate + L-aspartate = N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
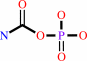 carbamoyl phosphate
carbamoyl phosphate
|
+
|
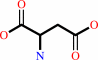 L-aspartate
L-aspartate
|
=
|
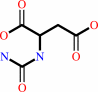 N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.2.3
- dihydroorotase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(S)-dihydroorotate + H2O = N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 (S)-dihydroorotate
(S)-dihydroorotate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
 N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
E.C.6.3.5.5
- carbamoyl-phosphate synthase (glutamine-hydrolyzing).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + L-glutamine + 2 ATP + H2O = carbamoyl phosphate + L-glutamate + 2 ADP + phosphate + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
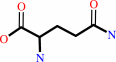 L-glutamine
L-glutamine
|
+
|
2
×
ATP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 75.00% similarity
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
 carbamoyl phosphate
carbamoyl phosphate
|
+
|
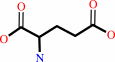 L-glutamate
L-glutamate
|
+
|
 2
×
ADP
2
×
ADP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
22:185-198
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure, functional characterization, and evolution of the dihydroorotase domain of human CAD.
|
|
A.Grande-García,
N.Lallous,
C.Díaz-Tejada,
S.Ramón-Maiques.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Upregulation of CAD, the multifunctional protein that initiates and controls the
de novo biosynthesis of pyrimidines in animals, is essential for cell
proliferation. Deciphering the architecture and functioning of CAD is of
interest for its potential usage as an antitumoral target. However, there is no
detailed structural information about CAD other than that it self-assembles
into hexamers of ∼1.5 MDa. Here we report the crystal structure and functional
characterization of the dihydroorotase domain of human CAD. Contradicting all
assumptions, the structure reveals an active site enclosed by a flexible loop
with two Zn(2+) ions bridged by a carboxylated lysine and a third Zn
coordinating a rare histidinate ion. Site-directed mutagenesis and functional
assays prove the involvement of the Zn and flexible loop in catalysis.
Comparison with homologous bacterial enzymes supports a reclassification of the
DHOase family and provides strong evidence against current models of the
architecture of CAD.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

