 |
PDBsum entry 4bc5
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.1.17
- xylulokinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-xylulose + ATP = D-xylulose 5-phosphate + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
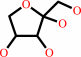 D-xylulose
D-xylulose
|
+
|
ATP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 81.82% similarity
|
=
|
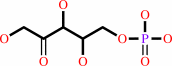 D-xylulose 5-phosphate
D-xylulose 5-phosphate
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Biol Chem
288:1643-1652
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure and function of human xylulokinase, an enzyme with important roles in carbohydrate metabolism.
|
|
R.D.Bunker,
E.M.Bulloch,
J.M.Dickson,
K.M.Loomes,
E.N.Baker.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
d-Xylulokinase (XK; EC 2.7.1.17) catalyzes the ATP-dependent phosphorylation of
d-xylulose (Xu) to produce xylulose 5-phosphate (Xu5P). In mammals, XK is the
last enzyme in the glucuronate-xylulose pathway, active in the liver and
kidneys, and is linked through its product Xu5P to the pentose-phosphate
pathway. XK may play an important role in metabolic disease, given that Xu5P is
a key regulator of glucose metabolism and lipogenesis. We have expressed the
product of a putative human XK gene and identified it as the authentic human
d-xylulokinase (hXK). NMR studies with a variety of sugars showed that hXK acts
only on d-xylulose, and a coupled photometric assay established its key kinetic
parameters as K(m)(Xu) = 24 ± 3 μm and k(cat) = 35 ± 5 s(-1). Crystal
structures were determined for hXK, on its own and in complexes with Xu, ADP,
and a fluorinated inhibitor. These reveal that hXK has a two-domain fold
characteristic of the sugar kinase/hsp70/actin superfamily, with glycerol kinase
as its closest relative. Xu binds to domain-I and ADP to domain-II, but in this
open form of hXK they are 10 Å apart, implying that a large scale
conformational change is required for catalysis. Xu binds in its linear
keto-form, sandwiched between a Trp side chain and polar side chains that
provide exquisite hydrogen bonding recognition. The hXK structure provides a
basis for the design of specific inhibitors with which to probe its roles in
sugar metabolism and metabolic disease.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

