 |
PDBsum entry 4xb2

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4xb2
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.3
- homoserine dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Threonine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
L-homoserine + NAD+ = L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde + NADH + H+
|
|
2.
|
L-homoserine + NADP+ = L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde + NADPH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-homoserine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 91.67% similarity
|
=
|
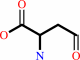 L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde
L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-homoserine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
 L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde
L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Sci Rep
5:11674
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal Structures of a Hyperthermophilic Archaeal Homoserine Dehydrogenase Suggest a Novel Cofactor Binding Mode for Oxidoreductases.
|
|
J.Hayashi,
S.Inoue,
K.Kim,
K.Yoneda,
Y.Kawarabayasi,
T.Ohshima,
H.Sakuraba.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
NAD(P)-dependent dehydrogenases differ according to their coenzyme preference:
some prefer NAD, others NADP, and still others exhibit dual cofactor
specificity. The structure of a newly identified archaeal homoserine
dehydrogenase showed this enzyme to have a strong preference for NADP. However,
NADP did not act as a cofactor with this enzyme, but as a strong inhibitor of
NAD-dependent homoserine oxidation. Structural analysis and site-directed
mutagenesis showed that the large number of interactions between the cofactor
and the enzyme are responsible for the lack of reactivity of the enzyme towards
NADP. This observation suggests this enzyme exhibits a new variation on cofactor
binding to a dehydrogenase: very strong NADP binding that acts as an obstacle to
NAD(P)-dependent dehydrogenase catalytic activity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

