 |
PDBsum entry 4w8c

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4w8c
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.8.4.11
- peptide-methionine (S)-S-oxide reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
L-methionyl-[protein] + [thioredoxin]-disulfide + H2O = L-methionyl- (S)-S-oxide-[protein] + [thioredoxin]-dithiol
|
|
2.
|
[thioredoxin]-disulfide + L-methionine + H2O = L-methionine (S)-S- oxide + [thioredoxin]-dithiol
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-methionyl-[protein]
|
+
|
[thioredoxin]-disulfide
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
L-methionyl- (S)-S-oxide-[protein]
|
+
|
[thioredoxin]-dithiol
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
[thioredoxin]-disulfide
|
+
|
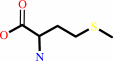 L-methionine
L-methionine
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 55.56% similarity
|
=
|
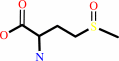 L-methionine (S)-S- oxide
L-methionine (S)-S- oxide
|
+
|
[thioredoxin]-dithiol
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Plos One
10:e0117836
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Essential role of the C-terminal helical domain in active site formation of selenoprotein MsrA from Clostridium oremlandii.
|
|
E.H.Lee,
K.Lee,
K.Y.Hwang,
H.Y.Kim.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
We previously determined the crystal structures of 1-Cys type selenoprotein MsrA
from Clostridium oremlandii (CoMsrA). The overall structure of CoMsrA is
unusual, consisting of two domains, the N-terminal catalytic domain and the
C-terminal distinct helical domain which is absent from other known MsrA
structures. Deletion of the helical domain almost completely abolishes the
catalytic activity of CoMsrA. In this study, we determined the crystal structure
of the helical domain-deleted (ΔH-domain) form of CoMsrA at a resolution of
1.76 Å. The monomer structure is composed of the central rolled mixed β-sheet
surrounded by α-helices. However, there are significant conformational changes
in the N- and C-termini and loop regions of the ΔH-domain protein relative to
the catalytic domain structure of full-length CoMsrA. The active site structure
in the ΔH-domain protein completely collapses, thereby causing loss of
catalytic activity of the protein. Interestingly, dimer structures are observed
in the crystal formed by N-terminus swapping between two molecules. The
ΔH-domain protein primarily exists as a dimer in solution, whereas the
full-length CoMsrA exists as a monomer. Collectively, this study provides
insight into the structural basis of the essential role of the helical domain of
CoMsrA in its catalysis.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

