 |
PDBsum entry 4qg9
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of pkm2-r399e mutant
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Pyruvate kinase pkm. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: cytosolic thyroid hormone-binding protein, cthbp, opa- interacting protein 3, oip-3, pyruvate kinase 2/3, pyruvate kinase muscle isozyme, thyroid hormone-binding protein 1, thbp1, tumor m2- pk, p58. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: pkm, oip3, pk2, pk3, pkm2. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.38Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.212
|
R-free:
|
0.256
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
P.Wang,C.Sun,T.Zhu,Y.Xu
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
P.Wang
et al.
(2015).
Structural insight into mechanisms for dynamic regulation of PKM2.
Protein Cell,
6,
275-287.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
22-May-14
|
Release date:
|
25-Feb-15
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D:
E.C.2.7.1.40
- pyruvate kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
pyruvate + ATP = phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 pyruvate
pyruvate
|
+
|
ATP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 66.67% similarity
|
=
|
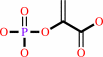 phosphoenolpyruvate
phosphoenolpyruvate
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D:
E.C.2.7.10.2
- non-specific protein-tyrosine kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-tyrosyl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-tyrosyl-[protein] + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-tyrosyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
O-phospho-L-tyrosyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D:
E.C.2.7.11.1
- non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
L-seryl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-seryl-[protein] + ADP + H+
|
|
2.
|
L-threonyl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein] + ADP + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-seryl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
O-phospho-L-seryl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-threonyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Protein Cell
6:275-287
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural insight into mechanisms for dynamic regulation of PKM2.
|
|
P.Wang,
C.Sun,
T.Zhu,
Y.Xu.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Pyruvate kinase isoform M2 (PKM2) converts phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to pyruvate
and plays an important role in cancer metabolism. Here, we show that
post-translational modifications and a patient-derived mutation regulate
pyruvate kinase activity of PKM2 through modulating the conformation of the PKM2
tetramer. We determined crystal structures of human PKM2 mutants and proposed a
"seesaw" model to illustrate conformational changes between an
inactive T-state and an active R-state tetramers of PKM2. Biochemical and
structural analyses demonstrate that PKM2(Y105E) (phosphorylation mimic of Y105)
decreases pyruvate kinase activity by inhibiting FBP (fructose
1,6-bisphosphate)-induced R-state formation, and PKM2(K305Q) (acetylation mimic
of K305) abolishes the activity by hindering tetramer formation. K422R, a
patient-derived mutation of PKM2, favors a stable, inactive T-state tetramer
because of strong intermolecular interactions. Our study reveals the mechanism
for dynamic regulation of PKM2 by post-translational modifications and a
patient-derived mutation and provides a structural basis for further
investigation of other modifications and mutations of PKM2 yet to be discovered.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

