 |
PDBsum entry 4qa6
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of i243n/y306f hdac8 in complex with a tetrapeptide substrate
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Histone deacetylase 8. Chain: a, b. Synonym: hd8. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes. Tetrapeptide substrate. Chain: c, d. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: hdac8, hdacl1, cda07. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008. Synthetic: yes. Other_details: synthetic peptide
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.05Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.182
|
R-free:
|
0.212
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
C.Decroos,C.B.Bowman,J.-A.S.Moser,K.E.Christianson,M.A.Deardorff, D.W.Christianson
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
C.Decroos
et al.
(2014).
Compromised structure and function of HDAC8 mutants identified in Cornelia de Lange Syndrome spectrum disorders.
Acs Chem Biol,
9,
2157-2164.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
02-May-14
|
Release date:
|
06-Aug-14
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q9BY41
(HDAC8_HUMAN) -
Histone deacetylase 8 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
377 a.a.
364 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 2 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.1.98
- histone deacetylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N6-acetyl-L-lysyl-[histone] + H2O = L-lysyl-[histone] + acetate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N(6)-acetyl-L-lysyl-[histone]
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
L-lysyl-[histone]
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 75.00% similarity
|
+
|
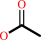 acetate
acetate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acs Chem Biol
9:2157-2164
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Compromised structure and function of HDAC8 mutants identified in Cornelia de Lange Syndrome spectrum disorders.
|
|
C.Decroos,
C.M.Bowman,
J.A.Moser,
K.E.Christianson,
M.A.Deardorff,
D.W.Christianson.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Cornelia de Lange Syndrome (CdLS) is a multiple congenital anomaly disorder
resulting from mutations in genes that encode the core components of the cohesin
complex, SMC1A, SMC3, and RAD21, or two of its regulatory proteins, NIPBL and
HDAC8. HDAC8 is the human SMC3 lysine deacetylase required for cohesin recycling
in the cell cycle. To date, 16 different missense mutations in HDAC8 have
recently been identified in children diagnosed with CdLS. To understand the
molecular effects of these mutations in causing CdLS and overlapping phenotypes,
we have fully characterized the structure and function of five HDAC8 mutants:
C153F, A188T, I243N, T311M, and H334R. X-ray crystal structures reveal that each
mutation causes local structural changes that compromise catalysis and/or
thermostability. For example, the C153F mutation triggers conformational changes
that block acetate product release channels, resulting in only 2% residual
catalytic activity. In contrast, the H334R mutation causes structural changes in
a polypeptide loop distant from the active site and results in 91% residual
activity, but the thermostability of this mutant is significantly compromised.
Strikingly, the catalytic activity of these mutants can be partially or fully
rescued in vitro by the HDAC8 activator N-(phenylcarbamothioyl)benzamide. These
results suggest that HDAC8 activators might be useful leads in the search for
new therapeutic strategies in managing CdLS.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

