 |
PDBsum entry 4pvc

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4pvc
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.265
- 3-methylbutanal reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
3-methylbutanol + NADP+ = 3-methylbutanal + NADPH + H+
|
|
2.
|
3-methylbutanol + NAD+ = 3-methylbutanal + NADH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
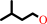 3-methylbutanol
3-methylbutanol
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
=
|
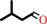 3-methylbutanal
3-methylbutanal
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
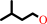 3-methylbutanol
3-methylbutanol
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
=
|
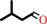 3-methylbutanal
3-methylbutanal
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.283
- methylglyoxal reductase (NADPH).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(S)-lactaldehyde + NADP+ = methylglyoxal + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
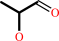 (S)-lactaldehyde
(S)-lactaldehyde
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
=
|
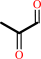 methylglyoxal
methylglyoxal
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochim Biophys Acta
1844:1486-1492
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural insights into the cofactor-assisted substrate recognition of yeast methylglyoxal/isovaleraldehyde reductase Gre2.
|
|
P.C.Guo,
Z.Z.Bao,
X.X.Ma,
Q.Xia,
W.F.Li.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Gre2 (EC1.1.1.283) serves as a versatile enzyme that
catalyzes the stereoselective reduction of a broad range of substrates including
aliphatic and aromatic ketones, diketones, as well as aldehydes, using NADPH as
the cofactor. Here we present the crystal structures of Gre2 from S. cerevisiae
in an apo-form at 2.00Å and NADPH-complexed form at 2.40Å resolution. Gre2
forms a homodimer, each subunit of which contains an N-terminal Rossmann-fold
domain and a variable C-terminal domain, which participates in substrate
recognition. The induced fit upon binding to the cofactor NADPH makes the two
domains shift toward each other, producing an interdomain cleft that better fits
the substrate. Computational simulation combined with site-directed mutagenesis
and enzymatic activity analysis enabled us to define a potential
substrate-binding pocket that determines the stringent substrate
stereoselectivity for catalysis.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

