 |
PDBsum entry 4p3n

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Ligase/ligase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4p3n
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Ligase/ligase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structural basis for full-spectrum inhibition of threonyl-tRNA synthetase by borrelidin 1
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Threonine--tRNA ligase, cytoplasmic. Chain: a, b, c, d. Fragment: unp residues 322-723. Synonym: threonyl-tRNA synthetase, thrrs. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: tars. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.60Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.229
|
R-free:
|
0.255
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
P.Fang,X.Yu,K.Chen,X.Chen,M.Guo
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
P.Fang
et al.
(2015).
Structural basis for full-spectrum inhibition of translational functions on a tRNA synthetase.
Nat Commun,
6,
6402.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
09-Mar-14
|
Release date:
|
11-Mar-15
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P26639
(SYTC_HUMAN) -
Threonine--tRNA ligase 1, cytoplasmic from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
723 a.a.
402 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.1.1.3
- threonine--tRNA ligase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
tRNA(Thr) + L-threonine + ATP = L-threonyl-tRNA(Thr) + AMP + diphosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
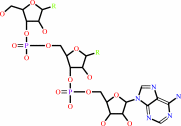 tRNA(Thr)
tRNA(Thr)
|
+
|
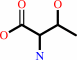 L-threonine
L-threonine
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
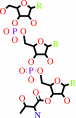 L-threonyl-tRNA(Thr)
L-threonyl-tRNA(Thr)
|
+
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Commun
6:6402
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis for full-spectrum inhibition of translational functions on a tRNA synthetase.
|
|
P.Fang,
X.Yu,
S.J.Jeong,
A.Mirando,
K.Chen,
X.Chen,
S.Kim,
C.S.Francklyn,
M.Guo.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The polyketide natural product borrelidin displays antibacterial, antifungal,
antimalarial, anticancer, insecticidal and herbicidal activities through the
selective inhibition of threonyl-tRNA synthetase (ThrRS). How borrelidin
simultaneously attenuates bacterial growth and suppresses a variety of
infections in plants and animals is not known. Here we show, using X-ray crystal
structures and functional analyses, that a single molecule of borrelidin
simultaneously occupies four distinct subsites within the catalytic domain of
bacterial and human ThrRSs. These include the three substrate-binding sites for
amino acid, ATP and tRNA associated with aminoacylation, and a fourth
'orthogonal' subsite created as a consequence of binding. Thus, borrelidin
competes with all three aminoacylation substrates, providing a potent and
redundant mechanism to inhibit ThrRS during protein synthesis. These results
highlight a surprising natural design to achieve the quadrivalent inhibition of
translation through a highly conserved family of enzymes.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

