 |
PDBsum entry 4n6e

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Lyase/biosynthetic protein
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4n6e
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase/biosynthetic protein
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of amycolatopsis orientalis bexx/cyso complex
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Putative thiosugar synthase. Chain: a. Engineered: yes. This/moad family protein. Chain: b. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Amycolatopsis orientalis. Organism_taxid: 797057. Strain: subsp. Vinearia. Gene: bexx. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008. Organism_taxid: 1156913. Strain: hccb10007. Gene: aori_6493.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.60Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.200
|
R-free:
|
0.240
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
X.Zhang,Y.Zhang,C.Kinsland,E.Sasaki,H.G.Sun,M.J.Lu,T.Liu,A.Ou,J.Li, Y.Chen,H.Liu,S.E.Ealick
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
E.Sasaki
et al.
(2014).
Co-opting sulphur-carrier proteins from primary metabolic pathways for 2-thiosugar biosynthesis.
Nature,
510,
427-431.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
11-Oct-13
|
Release date:
|
14-May-14
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chain A:
E.C.2.8.1.10
- thiazole synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[ThiS sulfur-carrier protein]-C-terminal-Gly-aminoethanethioate + 2-iminoacetate + 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate = [ThiS sulfur-carrier protein]-C-terminal Gly-Gly + 2-[(2R,5Z)-2-carboxy-4-methylthiazol-5(2H)- ylidene]ethyl phosphate + 2 H2O + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
[ThiS sulfur-carrier protein]-C-terminal-Gly-aminoethanethioate
|
+
|
2-iminoacetate
|
+
|
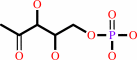 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate
1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate
|
=
|
[ThiS sulfur-carrier protein]-C-terminal Gly-Gly
|
+
|
2-[(2R,5Z)-2-carboxy-4-methylthiazol-5(2H)- ylidene]ethyl phosphate
|
+
|
2
×
H2O
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chain B:
E.C.?
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nature
510:427-431
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Co-opting sulphur-carrier proteins from primary metabolic pathways for 2-thiosugar biosynthesis.
|
|
E.Sasaki,
X.Zhang,
H.G.Sun,
M.Y.Lu,
T.L.Liu,
A.Ou,
J.Y.Li,
Y.H.Chen,
S.E.Ealick,
H.W.Liu.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Sulphur is an essential element for life and is ubiquitous in living systems.
Yet how the sulphur atom is incorporated into many sulphur-containing secondary
metabolites is poorly understood. For bond formation between carbon and sulphur
in primary metabolites, the major ionic sulphur sources are the persulphide and
thiocarboxylate groups on sulphur-carrier (donor) proteins. Each group is
post-translationally generated through the action of a specific activating
enzyme. In all reported bacterial cases, the gene encoding the enzyme that
catalyses the carbon-sulphur bond formation reaction and that encoding the
cognate sulphur-carrier protein exist in the same gene cluster. To study the
production of the 2-thiosugar moiety in BE-7585A, an antibiotic from
Amycolatopsis orientalis, we identified a putative 2-thioglucose synthase, BexX,
whose protein sequence and mode of action seem similar to those of ThiG, the
enzyme that catalyses thiazole formation in thiamine biosynthesis. However, no
gene encoding a sulphur-carrier protein could be located in the BE-7585A
cluster. Subsequent genome sequencing uncovered a few genes encoding
sulphur-carrier proteins that are probably involved in the biosynthesis of
primary metabolites but only one activating enzyme gene in the A. orientalis
genome. Further experiments showed that this activating enzyme can adenylate
each of these sulphur-carrier proteins and probably also catalyses the
subsequent thiolation, through its rhodanese domain. A proper combination of
these sulphur-delivery systems is effective for BexX-catalysed 2-thioglucose
production. The ability of BexX to selectively distinguish sulphur-carrier
proteins is given a structural basis using X-ray crystallography. This study is,
to our knowledge, the first complete characterization of thiosugar formation in
nature and also demonstrates the receptor promiscuity of the A. orientalis
sulphur-delivery system. Our results also show that co-opting the
sulphur-delivery machinery of primary metabolism for the biosynthesis of
sulphur-containing natural products is probably a general strategy found in
nature.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

