 |
PDBsum entry 4my4
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Isomerase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of phosphoglycerate mutase from staphylococcus aureus.
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
2,3-bisphosphoglycerate-independent phosphoglycerate mutase. Chain: a. Fragment: unp residues 3-505. Synonym: bpg-independent pgam, phosphoglyceromutase, ipgm. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Staphylococcus aureus subsp. Aureus. Organism_taxid: 93061. Strain: nctc8325. Gene: gpmi, saouhsc_00798. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.00Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.167
|
R-free:
|
0.216
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.Roychowdhury,A.Kundu,A.Gujar,M.Bose,A.K.Das
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
A.Roychowdhury
et al.
(2015).
Complete catalytic cycle of cofactor-independent phosphoglycerate mutase involves a spring-loaded mechanism.
Febs J,
282,
1097-1110.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
27-Sep-13
|
Release date:
|
16-Oct-13
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q2G029
(Q2G029_STAA8) -
2,3-bisphosphoglycerate-independent phosphoglycerate mutase from Staphylococcus aureus (strain NCTC 8325 / PS 47)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
505 a.a.
503 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.4.2.12
- phosphoglycerate mutase (2,3-diphosphoglycerate-independent).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(2R)-2-phosphoglycerate = (2R)-3-phosphoglycerate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
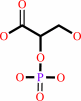 2-phospho-D-glycerate
2-phospho-D-glycerate
|
=
|
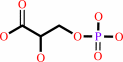 3-phospho-D-glycerate
3-phospho-D-glycerate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Cobalt cation or Mn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Febs J
282:1097-1110
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Complete catalytic cycle of cofactor-independent phosphoglycerate mutase involves a spring-loaded mechanism.
|
|
A.Roychowdhury,
A.Kundu,
M.Bose,
A.Gujar,
S.Mukherjee,
A.K.Das.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Cofactor-independent phosphoglycerate mutase (iPGM), an important enzyme in
glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, catalyses the isomerization of 2- and
3-phosphoglycerates by an Mn(2+) -dependent phospho-transfer mechanism via a
phospho-enzyme intermediate. Crystal structures of bi-domain iPGM from
Staphylococcus aureus, together with substrate-bound forms, have revealed a new
conformation of the enzyme, representing an intermediate state of domain
movement. The substrate-binding site and the catalytic site are present in two
distinct domains in the intermediate form. X-ray crystallography complemented by
simulated dynamics has enabled delineation of the complete catalytic cycle,
which includes binding of the substrate, followed by its positioning into the
catalytic site, phospho-transfer and finally product release. The present work
describes a novel mechanism of domain movement controlled by a hydrophobic patch
that is exposed on domain closure and acts like a spring to keep the protein in
open conformation. Domain closing occurs after substrate binding, and is
essential for phospho-transfer, whereas the open conformation is a prerequisite
for efficient substrate binding and product dissociation. A new model of
catalysis has been proposed by correlating the hinge-bending motion with the
phospho-transfer mechanism.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

