 |
PDBsum entry 4mvc
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of a mammalian cytidylyltransferase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase a. Chain: a, b. Fragment: cct1-312 (del 238-269). Synonym: cct-alpha, ctp:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase a, cct a, ct a, phosphorylcholine transferase a. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Rattus norvegicus. Brown rat,rat,rats. Organism_taxid: 10116. Gene: ctpct, pcyt1, pcyt1a. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
3.00Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.226
|
R-free:
|
0.288
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.Lee,R.B.Cornell
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.Lee
et al.
(2014).
Structural basis for autoinhibition of CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase (CCT), the regulatory enzyme in phosphatidylcholine synthesis, by its membrane-binding amphipathic helix.
J Biol Chem,
289,
1742-1755.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
23-Sep-13
|
Release date:
|
11-Dec-13
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P19836
(PCY1A_RAT) -
Choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase A from Rattus norvegicus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
367 a.a.
205 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.7.15
- choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
phosphocholine + CTP + H+ = CDP-choline + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
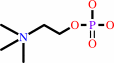 phosphocholine
phosphocholine
|
+
|
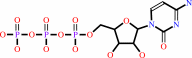 CTP
CTP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
CDP-choline
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
289:1742-1755
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis for autoinhibition of CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase (CCT), the regulatory enzyme in phosphatidylcholine synthesis, by its membrane-binding amphipathic helix.
|
|
J.Lee,
S.G.Taneva,
B.W.Holland,
D.P.Tieleman,
R.B.Cornell.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase (CCT) interconverts between an inactive
soluble and active membrane-bound form in response to changes in membrane lipid
composition. Activation involves disruption of an inhibitory interaction between
the αE helices at the base of the active site and an autoinhibitory (AI)
segment in the regulatory M domain and membrane insertion of the M domain as an
amphipathic helix. We show that in the CCT soluble form the AI segment functions
to suppress kcat and elevate the Km for CTP. The crystal structure of a CCT
dimer composed of the catalytic and AI segments reveals an AI-αE interaction as
a cluster of four amphipathic helices (two αE and two AI helices) at the base
of the active sites. This interaction corroborates mutagenesis implicating
multiple hydrophobic residues within the AI segment that contribute to its
silencing function. The AI-αE interaction directs the turn at the C-terminal
end of the AI helix into backbone-to-backbone contact with a loop (L2) at the
opening to the active site, which houses the key catalytic residue, lysine 122.
Molecular dynamics simulations suggest that lysine 122 side-chain orientations
are constrained by contacts with the AI helix-turn, which could obstruct its
engagement with substrates. This work deciphers how the CCT regulatory
amphipathic helix functions as a silencing device.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

