 |
PDBsum entry 4ltm

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4ltm
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.5.1.42
- Fmn reductase (NADH).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
FMNH2 + NAD+ = FMN + NADH + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
FMNH2
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
=
|
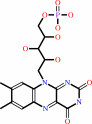 FMN
FMN
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
283:28710-28720
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal Structures of NADH:FMN Oxidoreductase (EmoB) at Different Stages of Catalysis.
|
|
M.S.Nissen,
B.Youn,
B.D.Knowles,
J.W.Ballinger,
S.Y.Jun,
S.M.Belchik,
L.Xun,
C.Kang.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
EDTA has become a major organic pollutant in the environment because of its
extreme usage and resistance to biodegradation. Recently, two critical enzymes,
EDTA monooxygenase (EmoA) and NADH:FMN oxidoreductase (EmoB), belonging to the
newly established two-component flavin-diffusible monooxygenase family, were
identified in the EDTA degradation pathway in Mesorhizobium sp. BNC1. EmoA is an
FMNH(2)-dependent enzyme that requires EmoB to provide FMNH(2) for the
conversion of EDTA to ethylenediaminediacetate. To understand the molecular
basis of this FMN-mediated reaction, the crystal structures of the apo-form,
FMN.FMN complex, and FMN.NADH complex of EmoB were determined at 2.5A
resolution. The structure of EmoB is a homotetramer consisting of four
alpha/beta-single-domain monomers of five parallel beta-strands flanked by five
alpha-helices, which is quite different from those of other known two-component
flavin-diffusible monooxygenase family members, such as PheA2 and HpaC, in terms
of both tertiary and quaternary structures. For the first time, the crystal
structures of both the FMN.FMN and FMN.NADH complexes of an NADH:FMN
oxidoreductase were determined. Two stacked isoalloxazine rings and
nicotinamide/isoalloxazine rings were at a proper distance for hydride transfer.
The structures indicated a ping-pong reaction mechanism, which was confirmed by
activity assays. Thus, the structural data offer detailed mechanistic
information for hydride transfer between NADH to an enzyme-bound FMN and between
the bound FMNH(2) and a diffusible FMN.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
EDTA and nitrilotriacetate (a structural homolog of EDTA)
degradation pathway. The enzymes are EDTA monooxygenase (encoded
by emoA), NADH:FMN oxidoreductase (emoB), and
ethylenediaminediacetate/iminodiacetate oxygenase (idaA). Each
enzymatic step removes an acetate group as a glyoxylate. ED3A,
ethylenediaminetriacetate; EDDA, ethylenediaminediacetate; EDMA,
ethylenediaminemonoacetate; ED, ethylenediamine; NTA,
nitrilotriacetate; IDA, iminodiacetate; Gly, glycine.
|
 |
Figure 5.
Measurement of FMN, riboflavin, or NADH binding by ITC
experiments. The trend of heat released by serial injections of
FMN (▪), riboflavin (▾), or NADH (•) into EmoB was
monitored. FMN showed the typical heat-releasing pattern.
Neither riboflavin nor NADH had any detectable heat-releasing
events upon injections. Solid lines represent the least-square
fits of the data using a single-site binding model.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
from an Open Access publication published by the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2008,
283,
28710-28720)
copyright 2008.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
B.N.Webb,
J.W.Ballinger,
E.Kim,
S.M.Belchik,
K.S.Lam,
B.Youn,
M.S.Nissen,
L.Xun,
and
C.Kang
(2010).
Characterization of chlorophenol 4-monooxygenase (TftD) and NADH:FAD oxidoreductase (TftC) of Burkholderia cepacia AC1100.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
285,
2014-2027.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Stokes-Rees,
and
P.Sliz
(2010).
Protein structure determination by exhaustive search of Protein Data Bank derived databases.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
21476-21481.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Binter,
N.Staunig,
I.Jelesarov,
K.Lohner,
B.A.Palfey,
S.Deller,
K.Gruber,
and
P.Macheroux
(2009).
A single intersubunit salt bridge affects oligomerization and catalytic activity in a bacterial quinone reductase.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
5263-5274.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

