 |
PDBsum entry 4jn6

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Lyase/oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4jn6
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase/oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of the aldolase-dehydrogenase complex from mycobacterium tuberculosis hrv37
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
4-hydroxy-2-oxovalerate aldolase. Chain: a, c. Synonym: hoa, 4-hydroxy-2-keto-pentanoic acid aldolase, 4-hydroxy-2- oxopentanoate aldolase. Engineered: yes. Acetaldehyde dehydrogenase. Chain: b, d. Synonym: acetaldehyde dehydrogenase [acetylating]. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Organism_taxid: 1773. Strain: hrv37. Gene: rv3534c, mt3638. Expressed in: rhodococcus jostii. Expression_system_taxid: 132919. Gene: mhpf, rv3535c, mt3639.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.93Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.176
|
R-free:
|
0.206
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.Carere,S.E.Mckenna,M.S.Kimber,S.Y.K.Seah
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.Carere
et al.
(2013).
Characterization of an aldolase-dehydrogenase complex from the cholesterol degradation pathway of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Biochemistry,
52,
3502-3511.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
14-Mar-13
|
Release date:
|
08-May-13
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
Chains A, C:
E.C.4.1.3.39
- 4-hydroxy-2-oxovalerate aldolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(S)-4-hydroxy-2-oxopentanoate = acetaldehyde + pyruvate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(S)-4-hydroxy-2-oxopentanoate
|
=
|
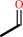 acetaldehyde
acetaldehyde
|
+
|
pyruvate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 71.43% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, C:
E.C.4.1.3.43
- 4-hydroxy-2-oxohexanoate aldolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(S)-4-hydroxy-2-oxohexanoate = propanal + pyruvate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(S)-4-hydroxy-2-oxohexanoate
|
=
|
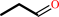 propanal
propanal
|
+
|
pyruvate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 71.43% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains B, D:
E.C.1.2.1.10
- acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (acetylating).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
acetaldehyde + NAD+ + CoA = acetyl-CoA + NADH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
acetaldehyde
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 50.00% similarity
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
=
|
 acetyl-CoA
acetyl-CoA
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
Chains B, D:
E.C.1.2.1.87
- propanal dehydrogenase (CoA-propanoylating).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
propanal + NAD+ + CoA = propanoyl-CoA + NADH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
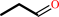 propanal
propanal
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
+
|
CoA
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 42.86% similarity
|
=
|
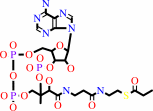 propanoyl-CoA
propanoyl-CoA
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
52:3502-3511
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Characterization of an aldolase-dehydrogenase complex from the cholesterol degradation pathway of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
|
|
J.Carere,
S.E.McKenna,
M.S.Kimber,
S.Y.Seah.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
HsaF and HsaG are an aldolase and dehydrogenase from the cholesterol degradation
pathway of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. HsaF could be heterologously expressed
and purified as a soluble dimer, but the enzyme was inactive in the absence of
HsaG. HsaF catalyzes the aldol cleavage of 4-hydroxy-2-oxoacids to produce
pyruvate and an aldehyde. The enzyme requires divalent metals for activity, with
a preference for Mn(2+). The Km values for 4-hydroxy-2-oxoacids were about
20-fold lower than observed for the aldolase homologue, BphI from the
polychlorinated biphenyl degradation pathway. Acetaldehyde and propionaldehyde
were channeled directly to the dehydrogenase, HsaG, without export to the bulk
solvent where they were transformed to acyl-CoA in an NAD(+) and coenzyme A
dependent reaction. HsaG is able to utilize aldehydes up to five carbons in
length as substrates, with similar catalytic efficiencies. The HsaF-HsaG complex
was crystallized and its structure was determined to a resolution of 1.93 Å.
Substitution of serine 41 in HsaG with isoleucine or aspartate resulted in about
35-fold increase in Km for CoA but only 4-fold increase in Km dephospho-CoA,
suggesting that this residue interacts with the 3'-ribose phosphate of CoA. A
second protein annotated as a 4-hydroxy-2-oxopentanoic acid aldolase in M.
tuberculosis (MhpE, Rv3469c) was expressed and purified, but was found to lack
aldolase activity. Instead this enzyme was found to possess oxaloacetate
decarboxylase activity, consistent with the conservation (with the
4-hydroxy-2-oxoacid aldolases) of residues involved in pyruvate enolate
stabilization.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

