 |
PDBsum entry 4ix8
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.2.6.1.5
- tyrosine transaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Phenylalanine and Tyrosine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-tyrosine + 2-oxoglutarate = 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)pyruvate + L-glutamate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
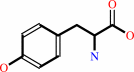 L-tyrosine
L-tyrosine
|
+
|
 2-oxoglutarate
2-oxoglutarate
|
=
|
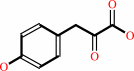 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)pyruvate
3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)pyruvate
|
+
|
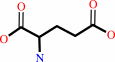 L-glutamate
L-glutamate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
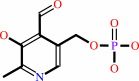 Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun
70:583-587
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of tyrosine aminotransferase from Leishmania infantum.
|
|
M.A.Moreno,
A.Abramov,
J.Abendroth,
A.Alonso,
S.Zhang,
P.J.Alcolea,
T.Edwards,
D.Lorimer,
P.J.Myler,
V.Larraga.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The trypanosomatid parasite Leishmania infantum is the causative agent of
visceral leishmaniasis (VL), which is usually fatal unless treated. VL has an
incidence of 0.5 million cases every year and is an important opportunistic
co-infection in HIV/AIDS. Tyrosine aminotransferase (TAT) has an important role
in the metabolism of trypanosomatids, catalyzing the first step in the
degradation pathway of aromatic amino acids, which are ultimately converted into
their corresponding L-2-oxoacids. Unlike the enzyme in Trypanosoma cruzi and
mammals, L. infantum TAT (LiTAT) is not able to transaminate ketoglutarate.
Here, the structure of LiTAT at 2.35 Å resolution is reported, and it is
confirmed that the presence of two Leishmania-specific residues (Gln55 and
Asn58) explains, at least in part, this specific reactivity. The difference in
substrate specificity between leishmanial and mammalian TAT and the importance
of this enzyme in parasite metabolism suggest that it may be a useful target in
the development of new drugs against leishmaniasis.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

