 |
PDBsum entry 4g7e
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.1.5
- urease.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
urea + 2 H2O + H+ = hydrogencarbonate + 2 NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
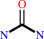 urea
urea
|
+
|
2
×
H2O
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
2
×
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Ni(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Int J Biol Macromol
58:301-309
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural and functional studies on urease from pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan).
|
|
A.Balasubramanian,
V.Durairajpandian,
S.Elumalai,
N.Mathivanan,
A.K.Munirajan,
K.Ponnuraj.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Urease is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of urea, forming ammonia and
carbon dioxide, and is found in plants, microorganisms and invertebrates.
Although plant and bacterial ureases are closely related at amino acid and at
the structural level, the insecticidal activity is seen only in the plant
ureases. In contrast, both plant and bacterial ureases exhibit antifungal
activity. These two biological properties are independent of its ureolytic
activity. However, till date the mechanism(s) behind the insecticidal and
fungicidal activity of ureases are not clearly understood. Here we report the
crystal structure of pigeon pea urease (PPU, Cajanus cajan) which is the second
structure from the plant source. We have deduced the amino acid sequence of PPU
and also report here studies on its stability, insecticidal and antifungal
activity. PPU exhibits cellulase activity. Based on the structural analysis of
PPU and docking studies with cellopentoase we propose a possible mechanism of
antifungal activity of urease.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

