 |
PDBsum entry 4g5e

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4g5e
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
2,4,6-trichlorophenol 4-monooxygenase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
2,4,6-trichlorophenol 4-monooxygenase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: 4-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Cupriavidus necator jmp134. Organism_taxid: 264198. Strain: jmp134 / lmg 1197. Gene: reut_a1585, tcpa. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.50Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.175
|
R-free:
|
0.224
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
R.P.Hayes,B.N.Webb,A.K.Subramanian,M.Nissen,A.Popchock,L.Xun,C.Kang
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
R.P.Hayes
et al.
(2012).
Structural and catalytic differences between two FADH(2)-dependent monooxygenases: 2,4,5-TCP 4-monooxygenase (TftD) from Burkholderia cepacia AC1100 and 2,4,6-TCP 4-monooxygenase (TcpA) from Cupriavidus necator JMP134.
Int J Mol Sci,
13,
9769-9784.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
17-Jul-12
|
Release date:
|
19-Sep-12
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q471I2
(Q471I2_CUPNJ) -
2,4,6-trichlorophenol monooxygenase from Cupriavidus pinatubonensis (strain JMP 134 / LMG 1197)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
517 a.a.
471 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.14.173
- 2,4,6-trichlorophenol monooxygenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2,4,6-trichlorophenol + FADH2 + O2 = 2-chloro-6-hydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone + FAD + 2 chloride + 3 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
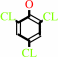 2,4,6-trichlorophenol
2,4,6-trichlorophenol
|
+
|
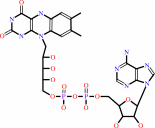 FADH2
FADH2
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
2-chloro-6-hydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone
|
+
|
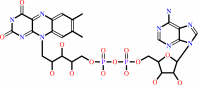 FAD
FAD
|
+
|
2
×
chloride
|
+
|
3
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Int J Mol Sci
13:9769-9784
(2012)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural and catalytic differences between two FADH(2)-dependent monooxygenases: 2,4,5-TCP 4-monooxygenase (TftD) from Burkholderia cepacia AC1100 and 2,4,6-TCP 4-monooxygenase (TcpA) from Cupriavidus necator JMP134.
|
|
R.P.Hayes,
B.N.Webb,
A.K.Subramanian,
M.Nissen,
A.Popchock,
L.Xun,
C.Kang.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
2,4,5-TCP 4-monooxygenase (TftD) and 2,4,6-TCP 4-monooxygenase (TcpA) have been
discovered in the biodegradation of 2,4,5-trichlorophenol (2,4,5-TCP) and
2,4,6-trichlorophenol (2,4,6-TCP). TcpA and TftD belong to the reduced flavin
adenine dinucleotide (FADH(2))-dependent monooxygenases and both use 2,4,6-TCP
as a substrate; however, the two enzymes produce different end products. TftD
catalyzes a typical monooxygenase reaction, while TcpA catalyzes a typical
monooxygenase reaction followed by a hydrolytic dechlorination. We have
previously reported the 3D structure of TftD and confirmed the catalytic
residue, His289. Here we have determined the crystal structure of TcpA and
investigated the apparent differences in specificity and catalysis between these
two closely related monooxygenases through structural comparison. Our
computational docking results suggest that Ala293 in TcpA (Ile292 in TftD) is
possibly responsible for the differences in substrate specificity between the
two monooxygenases. We have also identified that Arg101 in TcpA could provide
inductive effects/charge stabilization during hydrolytic dechlorination. The
collective information provides a fundamental understanding of the catalytic
reaction mechanism and the parameters for substrate specificity. The information
may provide guidance for designing bioremediation strategies for
polychlorophenols, a major group of environmental pollutants.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

