 |
PDBsum entry 4dao
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of the hexameric purine nucleoside phosphorylase from bacillus subtilis in complex with adenine
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase deod-type. Chain: a, b. Synonym: pnp, purine nucleoside phosphorylase ii, pu-npase ii. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Bacillus subtilis. Organism_taxid: 1423. Gene: bsu19630, deod, punb. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.22Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.151
|
R-free:
|
0.208
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
P.O.Giuseppe,N.H.Martins,A.N.Meza,M.T.Murakami
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
P.O.de Giuseppe
et al.
(2012).
Insights into phosphate cooperativity and influence of substrate modifications on binding and catalysis of hexameric purine nucleoside phosphorylases.
Plos One,
7,
e44282.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
13-Jan-12
|
Release date:
|
26-Sep-12
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
O34925
(DEOD_BACSU) -
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase DeoD-type from Bacillus subtilis (strain 168)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
233 a.a.
230 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.2.1
- purine-nucleoside phosphorylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
a purine D-ribonucleoside + phosphate = a purine nucleobase + alpha- D-ribose 1-phosphate
|
|
2.
|
a purine 2'-deoxy-D-ribonucleoside + phosphate = a purine nucleobase + 2-deoxy-alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
purine D-ribonucleoside
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
=
|
purine nucleobase
|
+
|
alpha- D-ribose 1-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 42.86% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
purine 2'-deoxy-D-ribonucleoside
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
=
|
purine nucleobase
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 46.15% similarity
|
+
|
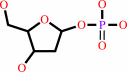 2-deoxy-alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate
2-deoxy-alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Plos One
7:e44282
(2012)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Insights into phosphate cooperativity and influence of substrate modifications on binding and catalysis of hexameric purine nucleoside phosphorylases.
|
|
P.O.de Giuseppe,
N.H.Martins,
A.N.Meza,
C.R.dos Santos,
H.D.Pereira,
M.T.Murakami.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The hexameric purine nucleoside phosphorylase from Bacillus subtilis (BsPNP233)
displays great potential to produce nucleoside analogues in industry and can be
exploited in the development of new anti-tumor gene therapies. In order to
provide structural basis for enzyme and substrates rational optimization, aiming
at those applications, the present work shows a thorough and detailed structural
description of the binding mode of substrates and nucleoside analogues to the
active site of the hexameric BsPNP233. Here we report the crystal structure of
BsPNP233 in the apo form and in complex with 11 ligands, including clinically
relevant compounds. The crystal structure of six ligands (adenine,
2'deoxyguanosine, aciclovir, ganciclovir, 8-bromoguanosine, 6-chloroguanosine)
in complex with a hexameric PNP are presented for the first time. Our data
showed that free bases adopt alternative conformations in the BsPNP233 active
site and indicated that binding of the co-substrate (2'deoxy)ribose 1-phosphate
might contribute for stabilizing the bases in a favorable orientation for
catalysis. The BsPNP233-adenosine complex revealed that a hydrogen bond between
the 5' hydroxyl group of adenosine and Arg(43*) side chain contributes for the
ribosyl radical to adopt an unusual C3'-endo conformation. The structures with
6-chloroguanosine and 8-bromoguanosine pointed out that the Cl(6) and Br(8)
substrate modifications seem to be detrimental for catalysis and can be explored
in the design of inhibitors for hexameric PNPs from pathogens. Our data also
corroborated the competitive inhibition mechanism of hexameric PNPs by
tubercidin and suggested that the acyclic nucleoside ganciclovir is a better
inhibitor for hexameric PNPs than aciclovir. Furthermore, comparative structural
analyses indicated that the replacement of Ser(90) by a threonine in the B.
cereus hexameric adenosine phosphorylase (Thr(91)) is responsible for the lack
of negative cooperativity of phosphate binding in this enzyme.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

