 |
PDBsum entry 4cll
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of human soluble adenylyl cyclase in complex with bicarbonate
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Adenylate cyclase type 10. Chain: a. Fragment: catalytic domain, residues 1-469. Synonym: ah-related protein, adenylate cyclase homolog, germ cell soluble adenylyl cyclase, hsac, sac, testicular soluble adenylyl cyclase, soluble adenylyl cyclase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Expressed in: trichoplusia ni. Expression_system_taxid: 7111. Expression_system_cell_line: high five.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.70Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.163
|
R-free:
|
0.198
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.Kleinboelting,M.Weyand,C.Steegborn
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
S.Kleinboelting
et al.
(2014).
Crystal structures of human soluble adenylyl cyclase reveal mechanisms of catalysis and of its activation through bicarbonate.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
111,
3727-3732.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
15-Jan-14
|
Release date:
|
05-Mar-14
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q96PN6
(ADCYA_HUMAN) -
Adenylate cyclase type 10 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
1610 a.a.
459 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.6.1.1
- adenylate cyclase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
ATP = 3',5'-cyclic AMP + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
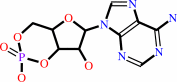 3',5'-cyclic AMP
3',5'-cyclic AMP
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
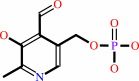 Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
111:3727-3732
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structures of human soluble adenylyl cyclase reveal mechanisms of catalysis and of its activation through bicarbonate.
|
|
S.Kleinboelting,
A.Diaz,
S.Moniot,
J.van den Heuvel,
M.Weyand,
L.R.Levin,
J.Buck,
C.Steegborn.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
cAMP is an evolutionary conserved, prototypic second messenger regulating
numerous cellular functions. In mammals, cAMP is synthesized by one of 10
homologous adenylyl cyclases (ACs): nine transmembrane enzymes and one soluble
AC (sAC). Among these, only sAC is directly activated by bicarbonate (HCO3(-));
it thereby serves as a cellular sensor for HCO3(-), carbon dioxide (CO2), and pH
in physiological functions, such as sperm activation, aqueous humor formation,
and metabolic regulation. Here, we describe crystal structures of human sAC
catalytic domains in the apo state and in complex with substrate analog,
products, and regulators. The activator HCO3(-) binds adjacent to Arg176, which
acts as a switch that enables formation of the catalytic cation sites. An
anionic inhibitor, 4,4'-diisothiocyanatostilbene-2,2'-disulfonic acid, inhibits
sAC through binding to the active site entrance, which blocks HCO3(-) activation
through steric hindrance and trapping of the Arg176 side chain. Finally, product
complexes reveal small, local rearrangements that facilitate catalysis. Our
results provide a molecular mechanism for sAC catalysis and cellular HCO3(-)
sensing and a basis for targeting this system with drugs.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

