 |
PDBsum entry 4ays
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.1.4
- amylosucrase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[(1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl](n) + sucrose = [(1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl](n+1) + D-fructose
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
[(1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl](n)
|
+
|
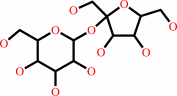 sucrose
sucrose
|
=
|
[(1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl](n+1)
|
+
|
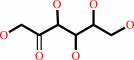 D-fructose
D-fructose
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun
69:973-978
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The structure of amylosucrase from Deinococcus radiodurans has an unusual open active-site topology.
|
|
L.K.Skov,
S.Pizzut-Serin,
M.Remaud-Simeon,
H.A.Ernst,
M.Gajhede,
O.Mirza.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Amylosucrases (ASes) catalyze the formation of an α-1,4-glucosidic linkage by
transferring a glucosyl unit from sucrose onto an acceptor α-1,4-glucan. To
date, several ligand-bound crystal structures of wild-type and mutant ASes from
Neisseria polysaccharea and Deinococcus geothermalis have been solved. These
structures all display a very similar overall conformation with a deep pocket
leading to the site for transglucosylation, subsite -1. This has led to
speculation on how sucrose enters the active site during glucan elongation. In
contrast to previous studies, the AS structure from D. radiodurans presented
here has a completely empty -1 subsite. This structure is strikingly different
from other AS structures, as an active-site-lining loop comprising residues
Leu214-Asn225 is found in a previously unobserved conformation. In addition, a
large loop harbouring the conserved active-site residues Asp133 and Tyr136 is
disordered. The result of the changed loop conformations is that the active-site
topology is radically changed, leaving subsite -1 exposed and partially
dismantled. This structure provides novel insights into the dynamics of ASes and
comprises the first structural support for an elongation mechanism that involves
considerable conformational changes to modulate accessibility to the
sucrose-binding site and thereby allows successive cycles of glucosyl-moiety
transfer to a growing glucan chain.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

