 |
PDBsum entry 3vpd
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.3.2.43
- [amino-group carrier protein]--L-2-aminoadipate ligase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[amino-group carrier protein]-C-terminal-L-glutamate + L-2-aminoadipate + ATP = [amino-group carrier protein]-C-terminal-N-(1,4-dicarboxybutan-1- yl)-L-glutamine + ADP + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
[amino-group carrier protein]-C-terminal-L-glutamate
|
+
|
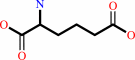 L-2-aminoadipate
L-2-aminoadipate
|
+
|
ATP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 41.18% similarity
|
=
|
[amino-group carrier protein]-C-terminal-N-(1,4-dicarboxybutan-1- yl)-L-glutamine
|
+
|
ADP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 81.25% similarity
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Chem Biol
9:277-283
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Lysine and arginine biosyntheses mediated by a common carrier protein in Sulfolobus.
|
|
T.Ouchi,
T.Tomita,
A.Horie,
A.Yoshida,
K.Takahashi,
H.Nishida,
K.Lassak,
H.Taka,
R.Mineki,
T.Fujimura,
S.Kosono,
C.Nishiyama,
R.Masui,
S.Kuramitsu,
S.V.Albers,
T.Kuzuyama,
M.Nishiyama.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
LysW has been identified as a carrier protein in the lysine biosynthetic pathway
that is active through the conversion of α-aminoadipate (AAA) to lysine. In
this study, we found that the hyperthermophilic archaeon, Sulfolobus
acidocaldarius, not only biosynthesizes lysine through LysW-mediated protection
of AAA but also uses LysW to protect the amino group of glutamate in arginine
biosynthesis. In this archaeon, after LysW modification, AAA and glutamate are
converted to lysine and ornithine, respectively, by a single set of enzymes with
dual functions. The crystal structure of ArgX, the enzyme responsible for
modification and protection of the amino moiety of glutamate with LysW, was
determined in complex with LysW. Structural comparison and enzymatic
characterization using Sulfolobus LysX, Sulfolobus ArgX and Thermus LysX
identify the amino acid motif responsible for substrate discrimination between
AAA and glutamate. Phylogenetic analysis reveals that gene duplication events at
different stages of evolution led to ArgX and LysX.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

