 |
PDBsum entry 3qna
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of a 6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase homologue from esherichia coli complexed sepiapterin
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
6-carboxy-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropterin synthase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f. Synonym: 6-carboxyterahydropterin synthase, ptps. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 469008. Strain: bl21(de3). Gene: ecdh1_0923. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.50Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.184
|
R-free:
|
0.230
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
K.H.Seo,N.N.Zhuang,K.H.Lee
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
K.H.Seo
et al.
(2014).
Structural basis of a novel activity of bacterial 6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase homologues distinct from mammalian 6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase activity.
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
70,
1212-1223.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
08-Feb-11
|
Release date:
|
07-Dec-11
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.2.50
- 6-carboxytetrahydropterin synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
7,8-dihydroneopterin 3'-triphosphate + H2O = 6-carboxy-5,6,7,8- tetrahydropterin + triphosphate + acetaldehyde + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
7,8-dihydroneopterin 3'-triphosphate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
6-carboxy-5,6,7,8- tetrahydropterin
|
+
|
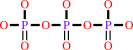 triphosphate
triphosphate
|
+
|
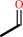 acetaldehyde
acetaldehyde
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
70:1212-1223
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis of a novel activity of bacterial 6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase homologues distinct from mammalian 6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase activity.
|
|
K.H.Seo,
N.Zhuang,
Y.S.Park,
K.H.Park,
K.H.Lee.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Escherichia coli 6-carboxytetrahydropterin synthase (eCTPS), a homologue of
6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase (PTPS), possesses a much stronger catalytic
activity to cleave the side chain of sepiapterin in vitro compared with genuine
PTPS activity and catalyzes the conversion of dihydroneopterin triphosphate to
6-carboxy-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropterin in vivo. Crystal structures of wild-type apo
eCTPS and of a Cys27Ala mutant eCTPS complexed with sepiapterin have been
determined to 2.3 and 2.5 Å resolution, respectively. The structures are
highly conserved at the active site and the Zn(2+) binding site. However,
comparison of the eCTPS structures with those of mammalian PTPS homologues
revealed that two specific residues, Trp51 and Phe55, that are not found in
mammalian PTPS keep the substrate bound by stacking it with their side chains.
Replacement of these two residues by site-directed mutagenesis to the residues
Met and Leu, which are only found in mammalian PTPS, converted eCTPS to the
mammalian PTPS activity. These studies confirm that these two aromatic residues
in eCTPS play an essential role in stabilizing the substrate and in the specific
enzyme activity that differs from the original PTPS activity. These aromatic
residues Trp51 and Phe55 are a key signature of bacterial PTPS enzymes that
distinguish them from mammalian PTPS homologues.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

