 |
PDBsum entry 3o4m

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Hydrolase/hydrolase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3o4m
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase/hydrolase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of porcine pancreatic phospholipase a2 in complex with 1,2-dihydroxybenzene
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Phospholipase a2, major isoenzyme. Chain: a. Synonym: phosphatidylcholine 2-acylhydrolase 1b, group ib phospholipase a2. Ec: 3.1.1.4
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Sus scrofa. Pig. Organism_taxid: 9823. Tissue: pancreas
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.50Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.184
|
R-free:
|
0.223
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
K.V.Dileep,I.Tintu,P.Karthe,P.K.Mandal,M.Haridas,C.Sadasivan
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
K.V.Dileep
et al.
(2012).
Binding to PLA2 may contribute to the anti-inflammatory activity of catechol.
Chem Biol Drug Des,
79,
143-147.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
27-Jul-10
|
Release date:
|
25-Aug-10
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P00592
(PA21B_PIG) -
Phospholipase A2, major isoenzyme from Sus scrofa
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
146 a.a.
124 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.4
- phospholipase A2.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine + H2O = a 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine + a fatty acid + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
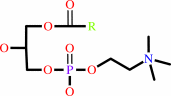 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
|
+
|
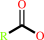 fatty acid
fatty acid
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Ca(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Chem Biol Drug Des
79:143-147
(2012)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Binding to PLA2 may contribute to the anti-inflammatory activity of catechol.
|
|
K.V.Dileep,
I.Tintu,
P.K.Mandal,
P.Karthe,
M.Haridas,
C.Sadasivan.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Inhibiting PLA(2) activity should, in theory, be an effective approach to
control the inflammation. Several naturally occurring polyphenolic compounds
have been reported as inhibitors of PLA(2) . Among the naturally occurring
polyphenols, catechol (1,2-dihydroxybenzene) possesses anti-inflammatory
activity. Catechol can inhibit cyclooxygenase and lipo-oxygenase. By means of
enzyme kinetic study, it was revealed that catechol can inhibit PLA(2) also.
Crystal structure showed that catechol binds to PLA(2) at the opening of the
active site cleft. This might stop the entry of substrate into the active site.
Hence, catechol can be used as a lead compound for the development of novel
anti-inflammatory drugs with PLA(2) as the target.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

