 |
PDBsum entry 3it4

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
The crystal structure of ornithine acetyltransferase from mycobacterium tuberculosis (rv1653) at 1.7 a
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Arginine biosynthesis bifunctional protein argj alpha chain. Chain: a, c. Synonym: glutamate n-acetyltransferase, ornithine acetyltransferase, oatase, ornithine transacetylase. Engineered: yes. Arginine biosynthesis bifunctional protein argj beta chain. Chain: b, d. Synonym: amino-acid acetyltransferase, n-acetylglutamate synthase,
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Organism_taxid: 1773. Strain: h37rv. Gene: argj, mt1691, mtcy06h11.18, rv1653. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Gene: argj, rv1653, mt1691, mtcy06h11.18.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.70Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.206
|
R-free:
|
0.244
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
R.Sankaranarayanan,M.M.Cherney,C.Garen,G.Garen,M.Yuan,M.N.James,Tb Structural Genomics Consortium (Tbsgc)
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
R.Sankaranarayanan
et al.
(2010).
The molecular structure of ornithine acetyltransferase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis bound to ornithine, a competitive inhibitor.
J Mol Biol,
397,
979-990.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
27-Aug-09
|
Release date:
|
02-Mar-10
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D:
E.C.2.3.1.1
- amino-acid N-acetyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Ornithine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-glutamate + acetyl-CoA = N-acetyl-L-glutamate + CoA + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
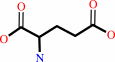 L-glutamate
L-glutamate
|
+
|
acetyl-CoA
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 58.33% similarity
|
=
|
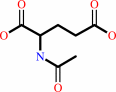 N-acetyl-L-glutamate
N-acetyl-L-glutamate
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D:
E.C.2.3.1.35
- glutamate N-acetyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N2-acetyl-L-ornithine + L-glutamate = N-acetyl-L-glutamate + L-ornithine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
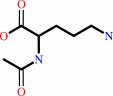 N(2)-acetyl-L-ornithine
N(2)-acetyl-L-ornithine
|
+
|
 L-glutamate
L-glutamate
|
=
|
N-acetyl-L-glutamate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 63.64% similarity
|
+
|
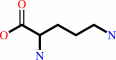 L-ornithine
L-ornithine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Mol Biol
397:979-990
(2010)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The molecular structure of ornithine acetyltransferase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis bound to ornithine, a competitive inhibitor.
|
|
R.Sankaranarayanan,
M.M.Cherney,
C.Garen,
G.Garen,
C.Niu,
M.Yuan,
M.N.James.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Mycobacterium tuberculosis ornithine acetyltransferase (Mtb OAT; E.C. 2.3.1.35)
is a key enzyme of the acetyl recycling pathway during arginine biosynthesis. It
reversibly catalyzes the transfer of the acetyl group from N-acetylornithine
(NAORN) to L-glutamate. Mtb OAT is a member of the N-terminal nucleophile fold
family of enzymes. The crystal structures of Mtb OAT in native form and in its
complex with ornithine (ORN) have been determined at 1.7 and 2.4 A resolutions,
respectively. ORN is a competitive inhibitor of this enzyme against L-glutamate
as substrate. Although the acyl-enzyme complex of Streptomyces clavuligerus
ornithine acetyltransferase has been determined, ours is the first crystal
structure to be reported of an ornithine acetyltransferase in complex with an
inhibitor. ORN binding does not alter the structure of Mtb OAT globally.
However, its presence stabilizes the three C-terminal residues that are
disordered and not observed in the native structure. Also, stabilization of the
C-terminal residues by ORN reduces the size of the active-site pocket volume in
the structure of the ORN complex. The interactions of ORN and the protein
residues of Mtb OAT unambiguously delineate the active-site residues of this
enzyme in Mtb. Moreover, modeling studies carried out with NAORN based on the
structure of the ORN-Mtb OAT complex reveal important interactions of the
carbonyl oxygen of the acetyl group of NAORN with the main-chain nitrogen atom
of Gly128 and with the side-chain oxygen of Thr127. These interactions likely
help in the stabilization of oxyanion formation during enzymatic reaction and
also will polarize the carbonyl carbon-oxygen bond, thereby enabling the
side-chain atom O(gamma 1) of Thr200 to launch a nucleophilic attack on the
carbonyl-carbon atom of the acetyl group of NAORN.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

