 |
PDBsum entry 3h4h

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3h4h
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.7.2.1
- nitrite reductase (NO-forming).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
nitric oxide + Fe(III)-[cytochrome c] + H2O = Fe(II)-[cytochrome c] + nitrite + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 nitric oxide
nitric oxide
|
+
|
Fe(III)-[cytochrome c]
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
Fe(II)-[cytochrome c]
|
+
|
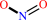 nitrite
nitrite
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Cu cation or Fe cation; FAD
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cu cation
|
or
|
Fe cation
|
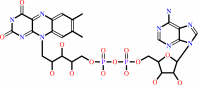 FAD
FAD
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Protein Eng Des Sel
23:137-145
(2010)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Directed evolution of copper nitrite reductase to a chromogenic reductant.
|
|
I.S.MacPherson,
F.I.Rosell,
M.Scofield,
A.G.Mauk,
M.E.Murphy.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Directed evolution methods were developed for Cu-containing nitrite reductase
(NiR) from Alcaligenes faecalis S-6. The PCR cloning strategy allows for the
efficient production of libraries of 100 000 clones by a modification of a
megaprimer-based whole-plasmid synthesis reaction. The high-throughput screen
includes colony lift onto a nylon membrane and subsequent lysis of
NiR-expressing colonies in the presence of Cu(2+) ions for copper incorporation
into intracellularly expressed NiR. Addition of a chromogenic substrate, 3,
3'-diaminobenzidine (DAB), results in deposition of red, insoluble color at the
site of oxidation by functional NiR. Twenty-thousand random variants of NiR were
screened for improved function with DAB as a reductant, and five variants were
identified. These variants were shuffled and screened, yielding two double
variants. An analog of the DAB substrate, o-dianisidine, which is oxidized to a
water-soluble product was used for functional characterization. The double
variant M150L/F312C was most proficient at o-dianisidine oxidation with dioxygen
as the electron acceptor (5.5X wt), and the M150L single variant was most
proficient at o-dianisidine oxidation with nitrite as the electron acceptor
(8.5X wt). The library generation and screening method can be employed for
evolving new reductase functions in NiR and for screening of efficient folding
of engineered NiRs.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

