 |
PDBsum entry 3gdk

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of the orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase from saccharomyces cerevisiae
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: omp decarboxylase, ompdecase, ompdcase, uridine 5'- monophosphate synthase, ump synthase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. Organism_taxid: 4932. Gene: ura3, yel021w. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.00Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.249
|
R-free:
|
0.280
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.A.Fedorov,E.V.Fedorov,B.M.Wood,J.A.Gerlt,S.C.Almo
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
K.K.Chan
et al.
(2009).
Mechanism of the orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase-catalyzed reaction: evidence for substrate destabilization.
Biochemistry,
48,
5518-5531.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
24-Feb-09
|
Release date:
|
23-Jun-09
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P03962
(PYRF_YEAST) -
Orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
267 a.a.
260 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.1.23
- orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Pyrimidine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
orotidine 5'-phosphate + H+ = UMP + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 orotidine 5'-phosphate
orotidine 5'-phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
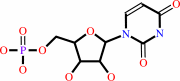 UMP
UMP
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
48:5518-5531
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Mechanism of the orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase-catalyzed reaction: evidence for substrate destabilization.
|
|
K.K.Chan,
B.M.Wood,
A.A.Fedorov,
E.V.Fedorov,
H.J.Imker,
T.L.Amyes,
J.P.Richard,
S.C.Almo,
J.A.Gerlt.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The reaction catalyzed by orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase (OMPDC)
involves a stabilized anionic intermediate, although the structural basis for
the rate acceleration (k(cat)/k(non), 7.1 x 10(16)) and proficiency
[(k(cat)/K(M))/k(non), 4.8 x 10(22) M(-1)] is uncertain. That the OMPDCs from
Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus (MtOMPDC) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae
(ScOMPDC) catalyze the exchange of H6 of the UMP product with solvent deuterium
allows an estimate of a lower limit on the rate acceleration associated with
stabilization of the intermediate and its flanking transition states
(>or=10(10)). The origin of the "missing" contribution, <or=10(7) (
approximately 10(17) total - >or=10(10)), is of interest. Based on structures
of liganded complexes, unfavorable electrostatic interactions between the
substrate carboxylate group and a proximal Asp (Asp 70 in MtOMPDC and Asp 91 in
ScOMPDC) have been proposed to contribute to the catalytic efficiency [Wu, N.,
Mo, Y., Gao, J., and Pai, E. F. (2000) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97,
2017-2022]. We investigated that hypothesis by structural and functional
characterization of the D70N and D70G mutants of MtOMPDC and the D91N mutant of
ScOMPDC. The substitutions for Asp 70 in MtOMPDC significantly decrease the
value of k(cat) for decarboxylation of FOMP (a more reactive substrate analogue)
but have little effect on the value of k(ex) for exchange of H6 of FUMP with
solvent deuterium; the structures of wild-type MtOMPDC and its mutants are
superimposable when complexed with 6-azaUMP. In contrast, the D91N mutant of
ScOMPDC does not catalyze exchange of H6 of FUMP; the structures of wild-type
ScOMPDC and its D91N mutant are not superimposable when complexed with 6-azaUMP,
with differences in both the conformation of the active site loop and the
orientation of the ligand vis a vis the active site residues. We propose that
the differential effects of substitutions for Asp 70 of MtOMPDC on
decarboxylation and exchange provide additional evidence for a carbanionic
intermediate as well as the involvement of Asp 70 in substrate destabilization.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
S.Thirumalairajan,
B.Mahaney,
and
S.L.Bearne
(2010).
Interrogation of the active site of OMP decarboxylase from Escherichia coli with a substrate analogue bearing an anionic group at C6.
|
| |
Chem Commun (Camb),
46,
3158-3160.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Lewis,
and
R.Wolfenden
(2009).
Orotic acid decarboxylation in water and nonpolar solvents: a potential role for desolvation in the action of OMP decarboxylase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
8738-8745.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Toth,
T.L.Amyes,
B.M.Wood,
K.K.Chan,
J.A.Gerlt,
and
J.P.Richard
(2009).
An examination of the relationship between active site loop size and thermodynamic activation parameters for orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase from mesophilic and thermophilic organisms.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
8006-8013.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

