 |
PDBsum entry 3fcc

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.2.1.54
- D-alanine--[D-alanyl-carrier protein] ligase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
holo-[D-alanyl-carrier protein] + D-alanine + ATP = D-alanyl-[D-alanyl- carrier protein] + AMP + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
holo-[D-alanyl-carrier protein]
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
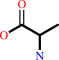 D-alanine
D-alanine
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
D-alanyl-[D-alanyl- carrier protein]
|
+
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
388:345-355
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of Bacillus cereus D-alanyl carrier protein ligase (DltA) in complex with ATP.
|
|
K.T.Osman,
L.Du,
Y.He,
Y.Luo.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
D-alanylation of lipoteichoic acids modulates the surface charge and ligand
binding of the Gram-positive cell wall. Disruption of the bacterial dlt operon
involved in teichoic acid alanylation, as well as inhibition of the DltA
(D-alanyl carrier protein ligase) protein, has been shown to render the
bacterium more susceptible to conventional antibiotics and host defense
responses. The DltA catalyzes the adenylation and thiolation reactions of
d-alanine. This enzyme belongs to a superfamily of AMP-forming domains such as
the ubiquitous acetyl-coenzyme A synthetase. We have determined the
1.9-A-resolution crystal structure of a DltA protein from Bacillus cereus in
complex with ATP. This structure sheds light on the geometry of the bound ATP.
The invariant catalytic residue Lys492 appears to be mobile, suggesting a
molecular mechanism of catalysis for this superfamily of enzymes. Specific roles
are also revealed for two other invariant residues: the divalent
cation-stabilizing Glu298 and the beta-phosphate-interacting Arg397. Mutant
proteins with a glutamine substitution at position 298 or 397 are inactive.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
Fig. 3. Structural comparison of DltA and human medium-chain
ACS in stereo. The superimposed ATP-binding pockets are shown.
The BcDltA model is shown as in Fig. 2c. The counterparts in the
human ACS are shown in gray.
|
 |
Figure 5.
Fig. 5. Adenylation model in stereo. The model was based on
the BcDltA/ATP structure and the BcDltA/adenylate structure. The
orientation and coloring scheme are similar to those in Fig. 2b.
The  epsilon
-amino group of the mobile Lys492 residue escorts the electron
transfer from the nucleophilic d-alanyl carboxylate group via a
pentavalent transition state to the leaving pyrophosphate. epsilon
-amino group of the mobile Lys492 residue escorts the electron
transfer from the nucleophilic d-alanyl carboxylate group via a
pentavalent transition state to the leaving pyrophosphate.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2009,
388,
345-355)
copyright 2009.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|

|
| |
The mobile Lysine appears to be critical in escorting the developing negative charge along the reaction pathway.
|
|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.K.Bera,
V.Atanasova,
S.Gamage,
H.Robinson,
and
J.F.Parsons
(2010).
Structure of the D-alanylgriseoluteic acid biosynthetic protein EhpF, an atypical member of the ANL superfamily of adenylating enzymes.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
66,
664-672.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.M.Gulick
(2009).
Conformational dynamics in the Acyl-CoA synthetases, adenylation domains of non-ribosomal peptide synthetases, and firefly luciferase.
|
| |
ACS Chem Biol,
4,
811-827.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.B.Shah,
C.Ingram-Smith,
L.L.Cooper,
J.Qu,
Y.Meng,
K.S.Smith,
and
A.M.Gulick
(2009).
The 2.1 A crystal structure of an acyl-CoA synthetase from Methanosarcina acetivorans reveals an alternate acyl-binding pocket for small branched acyl substrates.
|
| |
Proteins,
77,
685-698.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

