 |
PDBsum entry 3ewc

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.4.31
- S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine deaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine + H2O + H+ = S-methyl-5'-thioinosine + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
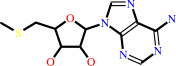 S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine
S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine
|
+
|
H2O
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 70.83% similarity
|
=
|
S-methyl-5'-thioinosine
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.4.4
- adenosine deaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
adenosine + H2O + H+ = inosine + NH4+
|
|
2.
|
2'-deoxyadenosine + H2O + H+ = 2'-deoxyinosine + NH4+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
adenosine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 73.91% similarity
|
+
|
H2O
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
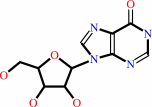 inosine
inosine
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
2'-deoxyadenosine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 69.57% similarity
|
+
|
H2O
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
2'-deoxyinosine
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
48:9618-9626
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural and metabolic specificity of methylthiocoformycin for malarial adenosine deaminases.
|
|
M.C.Ho,
M.B.Cassera,
D.C.Madrid,
L.M.Ting,
P.C.Tyler,
K.Kim,
S.C.Almo,
V.L.Schramm.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Plasmodium falciparum is a purine auxotroph requiring hypoxanthine as a key
metabolic precursor. Erythrocyte adenine nucleotides are the source of the
purine precursors, making adenosine deaminase (ADA) a key enzyme in the pathway
of hypoxanthine formation. Methylthioadenosine (MTA) is a substrate for most
malarial ADAs, but not for human ADA. The catalytic site specificity of malarial
ADAs permits methylthiocoformycin (MT-coformycin) to act as a
Plasmodium-specific transition state analogue with low affinity for human ADA
[Tyler, P. C., Taylor, E. A., Frohlich, R. G. G., and Schramm, V. L. (2007) J.
Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 6872-6879]. The structural basis for MTA and MT-coformycin
specificity in malarial ADAs is the subject of speculation [Larson, E. T., et
al. (2008) J. Mol. Biol. 381, 975-988]. Here, the crystal structure of ADA from
Plasmodium vivax (PvADA) in a complex with MT-coformycin reveals an
unprecedented binding geometry for 5'-methylthioribosyl groups in the malarial
ADAs. Compared to malarial ADA complexes with adenosine or deoxycoformycin,
5'-methylthioribosyl groups are rotated 130 degrees . A hydrogen bonding network
between Asp172 and the 3'-hydroxyl of MT-coformycin is essential for recognition
of the 5'-methylthioribosyl group. Water occupies the 5'-hydroxyl binding site
when MT-coformycin is bound. Mutagenesis of Asp172 destroys the substrate
specificity for MTA and MT-coformycin. Kinetic, mutagenic, and structural
analyses of PvADA and kinetic analysis of five other Plasmodium ADAs establish
the unique structural basis for its specificity for MTA and MT-coformycin.
Plasmodium gallinaceum ADA does not use MTA as a substrate, is not inhibited by
MT-coformycin, and is missing Asp172. Treatment of P. falciparum cultures with
coformycin or MT-coformycin in the presence of MTA is effective in inhibiting
parasite growth.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
G.Plata,
T.L.Hsiao,
K.L.Olszewski,
M.Llinás,
and
D.Vitkup
(2010).
Reconstruction and flux-balance analysis of the Plasmodium falciparum metabolic network.
|
| |
Mol Syst Biol,
6,
408.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

