 |
PDBsum entry 3ekd

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3ekd
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.14.1
- unspecific monooxygenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an organic molecule + reduced [NADPH--hemoprotein reductase] + O2 = an alcohol + oxidized [NADPH--hemoprotein reductase] + H2O + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
organic molecule
|
+
|
reduced [NADPH--hemoprotein reductase]
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
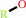 alcohol
alcohol
|
+
|
oxidized [NADPH--hemoprotein reductase]
|
+
|
H2O
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Heme-thiolate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.1.6.2.4
- NADPH--hemoprotein reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2 oxidized [cytochrome P450] + NADPH = 2 reduced [cytochrome P450] + NADP+ + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
2
×
oxidized [cytochrome P450]
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
=
|
2
×
reduced [cytochrome P450]
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD; FMN
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 FAD
FAD
|
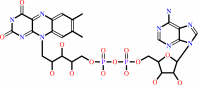
 FMN
FMN
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochem J
417:65-76
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Novel haem co-ordination variants of flavocytochrome P450BM3.
|
|
H.M.Girvan,
H.S.Toogood,
R.E.Littleford,
H.E.Seward,
W.E.Smith,
I.S.Ekanem,
D.Leys,
M.R.Cheesman,
A.W.Munro.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Bacillus megaterium flavocytochrome P450 BM3 is a catalytically self-sufficient
fatty acid hydroxylase formed by fusion of soluble NADPH-cytochrome P450
reductase and P450 domains. Selected mutations at residue 264 in the haem (P450)
domain of the enzyme lead to novel amino acid sixth (distal) co-ordination
ligands to the haem iron. The catalytic, spectroscopic and thermodynamic
properties of the A264M, A264Q and A264C variants were determined in both the
intact flavocytochromes and haem domains of P450 BM3. Crystal structures of the
mutant haem domains demonstrate axial ligation of P450 haem iron by methionine
and glutamine ligands trans to the cysteine thiolate, creating novel haem iron
ligand sets in the A264M/Q variants. In contrast, the crystal structure of the
A264C variant reveals no direct interaction between the introduced cysteine side
chain and the haem, although EPR data indicate Cys(264) interactions with haem
iron in solution. The A264M haem potential is elevated by comparison with
wild-type haem domain, and substrate binding to the A264Q haem domain results in
a approximately 360 mV increase in potential. All mutant haem domains occupy the
conformation adopted by the substrate-bound form of wild-type BM3, despite the
absence of added substrate. The A264M mutant (which has higher dodecanoate
affinity than wild-type BM3) co-purifies with a structurally resolved lipid.
These data demonstrate that a single mutation at Ala(264) is enough to perturb
the conformational equilibrium between substrate-free and substrate-bound P450
BM3, and provide firm structural and spectroscopic data for novel haem iron
ligand sets unprecedented in nature.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Whitehouse,
W.Yang,
J.A.Yorke,
B.C.Rowlatt,
A.J.Strong,
C.F.Blanford,
S.G.Bell,
M.Bartlam,
L.L.Wong,
and
Z.Rao
(2010).
Structural basis for the properties of two single-site proline mutants of CYP102A1 (P450BM3).
|
| |
Chembiochem,
11,
2549-2556.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.M.Girvan,
C.W.Levy,
P.Williams,
K.Fisher,
M.R.Cheesman,
S.E.Rigby,
D.Leys,
and
A.W.Munro
(2010).
Glutamate-haem ester bond formation is disfavoured in flavocytochrome P450 BM3: characterization of glutamate substitution mutants at the haem site of P450 BM3.
|
| |
Biochem J,
427,
455-466.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.C.Pochapsky,
S.Kazanis,
and
M.Dang
(2010).
Conformational plasticity and structure/function relationships in cytochromes P450.
|
| |
Antioxid Redox Signal,
13,
1273-1296.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Whitehouse,
S.G.Bell,
W.Yang,
J.A.Yorke,
C.F.Blanford,
A.J.Strong,
E.J.Morse,
M.Bartlam,
Z.Rao,
and
L.L.Wong
(2009).
A highly active single-mutation variant of P450BM3 (CYP102A1).
|
| |
Chembiochem,
10,
1654-1656.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

