 |
PDBsum entry 3ea3

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of the y246s/y247s/y248s/y251s mutant of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipasE C from bacillus thuringiensis
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
1-phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: phosphatidylinositol diacylglycerol-lyase, phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipasE C, pi-plc. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Bacillus thuringiensis. Organism_taxid: 1428. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.78Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.185
|
R-free:
|
0.221
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
X.Shi,C.Shao,X.Zhang,C.Zambonelli,A.G.Redfied,J.F.Head,B.A.Seaton, M.F.Roberts
|
Key ref:

|
 |
X.Shi
et al.
(2009).
Modulation of bacillus thuringiensis phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity by mutations in the putative dimerization interface.
J Biol Chem,
284,
15607-15618.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
24-Aug-08
|
Release date:
|
14-Apr-09
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P08954
(PLC_BACTU) -
1-phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase from Bacillus thuringiensis
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
329 a.a.
296 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 4 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.6.1.13
- phosphatidylinositol diacylglycerol-lyase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
1-Phosphatidyl-myo-inositol Metabolism
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1D-myo-inositol) = 1D-myo-inositol 1,2-cyclic phosphate + a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1D-myo-inositol)
|
=
|
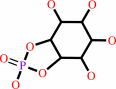 1D-myo-inositol 1,2-cyclic phosphate
1D-myo-inositol 1,2-cyclic phosphate
|
+
|
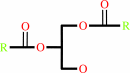 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
284:15607-15618
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Modulation of bacillus thuringiensis phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity by mutations in the putative dimerization interface.
|
|
X.Shi,
C.Shao,
X.Zhang,
C.Zambonelli,
A.G.Redfield,
J.F.Head,
B.A.Seaton,
M.F.Roberts.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Cleavage of phosphatidylinositol (PI) to inositol 1,2-(cyclic)-phosphate (cIP)
and cIP hydrolysis to inositol-1-phosphate by Bacillus thuringiensis
phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) are activated by the
enzyme binding to phosphatidylcholine (PC) surfaces. Part of this reflects
improved binding of the protein to interfaces. However, crystallographic
analysis of an interfacially impaired PI-PLC (W47A/W242A) suggested protein
dimerization might occur on the membrane. In the W47A/W242A dimer, four tyrosine
residues from one monomer interact with the same tyrosine cluster of the other,
forming a tight dimer interface close to the membrane binding regions. We have
constructed mutant proteins in which two or more of these tyrosine residues have
been replaced with serine. Phospholipid binding and enzymatic activity of these
mutants have been examined in order to assess the importance of these residues
to enzyme function. Replacing two tyrosines had small effects on enzyme
activity. However, removal of three or four tyrosine residues weakened PC
binding and reduced PI cleavage by the enzyme as well as PC activation of cIP
hydrolysis. Crystal structures of Y247S/Y251S, in the absence and presence of
myo-inositol, as well as Y246S/Y247S/Y248S/Y251S indicate that both mutant
proteins crystallized as monomers, were very similar to one another, and had no
change in the active site region. Kinetic assays, lipid binding, and structural
results indicate that either (i) a specific PC binding site, critical for
vesicle activities and cIP activation, has been impaired, or (ii) the reduced
dimerization potential for Y246S/Y247S/Y248S and Y246S/Y247S/Y248S/Y251S is
responsible for their reduced catalytic activity in all assay systems.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Stereo structure of the mutation sites in B. thuringiensis
Y247S/Y251S PI-PLC. Shown in the gray network is the electron
density (from the simulated-annealing composite omit map and
contoured at 1.2σ) for the residues in mutation sites. The
helix hydrogen-bond network is shown as orange dotted lines.
|
 |
Figure 2.
Stereoview showing tyrosine mutation sites at the
crystallographic dimer interface of B. thuringiensis PI-PLC
mutant, W47A/W242A (PDB code 2OR2). Subunit A is shown with
Corey-Pauling-Koltun coloration, labels are in bold. subunit B
is shown in cyan, and labels are in italics. Hydrogen bonds
shown as green dashed lines.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2009,
284,
15607-15618)
copyright 2009.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.Pu,
M.F.Roberts,
and
A.Gershenson
(2009).
Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C monitors the interplay of substrate and activator lipid binding.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
6835-6845.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

