 |
PDBsum entry 3e12

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Cu2+ substituted aquifex aeolicus kdo8ps in complex with kdo8p
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
2-dehydro-3-deoxyphosphooctonate aldolase. Chain: a, b. Fragment: kdo8ps. Synonym: phospho-2-dehydro-3-deoxyoctonate aldolase, 3-deoxy-d-manno- octulosonic acid 8-phosphate synthetase, kdo-8-phosphate synthetase, kdo 8-p synthase, kdops. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Aquifex aeolicus. Organism_taxid: 63363. Gene: kdsa, aq_085. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.70Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.168
|
R-free:
|
0.196
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
D.L.Gatti
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
F.Kona
et al.
(2009).
Electronic structure of the metal center in the Cd(2+), Zn(2+), and Cu(2+) substituted forms of KDO8P synthase: implications for catalysis.
Biochemistry,
48,
3610-3630.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
01-Aug-08
|
Release date:
|
12-May-09
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
O66496
(KDSA_AQUAE) -
2-dehydro-3-deoxyphosphooctonate aldolase from Aquifex aeolicus (strain VF5)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
267 a.a.
258 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.55
- 3-deoxy-8-phosphooctulonate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-arabinose 5-phosphate + phosphoenolpyruvate + H2O = 3-deoxy-alpha-D- manno-2-octulosonate-8-phosphate + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
D-arabinose 5-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 70.00% similarity
|
+
|
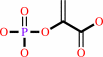 phosphoenolpyruvate
phosphoenolpyruvate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
3-deoxy-alpha-D- manno-2-octulosonate-8-phosphate
|
+
|
phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
48:3610-3630
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Electronic structure of the metal center in the Cd(2+), Zn(2+), and Cu(2+) substituted forms of KDO8P synthase: implications for catalysis.
|
|
F.Kona,
P.Tao,
P.Martin,
X.Xu,
D.L.Gatti.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Aquifex aeolicus 3-deoxy-d-manno-octulosonate 8-phosphate synthase (KDO8PS) is
active with a variety of different divalent metal ions bound in the active site.
The Cd(2+), Zn(2+), and Cu(2+) substituted enzymes display similar values of
k(cat) and similar dependence of K(m)(PEP) and K(m)(A5P) on both substrate and
product concentrations. However, the flux-control coefficients for some of the
catalytically relevant reaction steps are different in the presence of Zn(2+) or
Cu(2+), suggesting that the type of metal bound in the active site affects the
behavior of the enzyme in vivo. The type of metal also affects the rate of
product release in the crystal environment. For example, the crystal structure
of the Cu(2+) enzyme incubated with phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and arabinose
5-phosphate (A5P) shows the formed product, 3-deoxy-d-manno-octulosonate
8-phosphate (KDO8P), still bound in the active site in its linear conformation.
This observation completes our structural studies of the condensation reaction,
which altogether have provided high-resolution structures for the reactants, the
intermediate, and the product bound forms of KDO8PS. The crystal structures of
the Cd(2+), Zn(2+), and Cu(2+) substituted enzymes show four residues (Cys-11,
His-185, Glu-222, and Asp-233) and a water molecule as possible metal ligands.
Combined quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) geometry optimizations
reveal that the metal centers have a delocalized electronic structure, and that
their true geometry is square pyramidal for Cd(2+) and Zn(2+) and distorted
octahedral or distorted tetrahedral for Cu(2+). These geometries are different
from those obtained by QM optimization in the gas phase (tetrahedral for Cd(2+)
and Zn(2+), distorted tetrahedral for Cu(2+)) and may represent conformations of
the metal center that minimize the reorganization energy between the
substrate-bound and product-bound states. The QM/MM calculations also show that
when only PEP is bound to the enzyme the electronic structure of the metal
center is optimized to prevent a wasteful reaction of PEP with water.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

