 |
PDBsum entry 3dyh

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.10
- (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Terpenoid biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
isopentenyl diphosphate + (2E)-geranyl diphosphate = (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
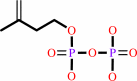 isopentenyl diphosphate
isopentenyl diphosphate
|
+
|
(2E)-geranyl diphosphate
|
=
|
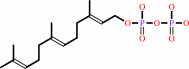 (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Am Chem Soc
131:5153-5162
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Lipophilic bisphosphonates as dual farnesyl/geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase inhibitors: an X-ray and NMR investigation.
|
|
Y.Zhang,
R.Cao,
F.Yin,
M.P.Hudock,
R.T.Guo,
K.Krysiak,
S.Mukherjee,
Y.G.Gao,
H.Robinson,
Y.Song,
J.H.No,
K.Bergan,
A.Leon,
L.Cass,
A.Goddard,
T.K.Chang,
F.Y.Lin,
E.Van Beek,
S.Papapoulos,
A.H.Wang,
T.Kubo,
M.Ochi,
D.Mukkamala,
E.Oldfield.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Considerable effort has focused on the development of selective protein farnesyl
transferase (FTase) and protein geranylgeranyl transferase (GGTase) inhibitors
as cancer chemotherapeutics. Here, we report a new strategy for anticancer
therapeutic agents involving inhibition of farnesyl diphosphate synthase (FPPS)
and geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase (GGPPS), the two enzymes upstream of
FTase and GGTase, by lipophilic bisphosphonates. Due to dual site targeting and
decreased polarity, the compounds have activities far greater than do current
bisphosphonate drugs in inhibiting tumor cell growth and invasiveness, both in
vitro and in vivo. We explore how these compounds inhibit cell growth and how
cell activity can be predicted based on enzyme inhibition data, and using X-ray
diffraction, solid state NMR, and isothermal titration calorimetry, we show how
these compounds bind to FPPS and/or GGPPS.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
P.Canepa,
F.Chiatti,
M.Corno,
Y.Sakhno,
G.Martra,
and
P.Ugliengo
(2011).
Affinity of hydroxyapatite (001) and (010) surfaces to formic and alendronic acids: a quantum-mechanical and infrared study.
|
| |
Phys Chem Chem Phys,
13,
1099-1111.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.J.Falconer,
and
B.M.Collins
(2011).
Survey of the year 2009: applications of isothermal titration calorimetry.
|
| |
J Mol Recognit,
24,
1.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.P.Singh,
Y.Zhang,
J.H.No,
R.Docampo,
V.Nussenzweig,
and
E.Oldfield
(2010).
Lipophilic bisphosphonates are potent inhibitors of Plasmodium liver-stage growth.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
54,
2987-2993.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Maltezou,
M.Stylianou,
S.Roy,
C.Drouza,
and
A.D.Keramidas
(2010).
Synthesis, solution, and structural characterization of tetrahydrofuranyl-2,2-bisphosphonic acid disodium salt.
|
| |
Bioinorg Chem Appl,
(),
563875.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Oldfield
(2010).
Targeting isoprenoid biosynthesis for drug discovery: bench to bedside.
|
| |
Acc Chem Res,
43,
1216-1226.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.D.Compain,
P.Mialane,
J.Marrot,
F.Sécheresse,
W.Zhu,
E.Oldfield,
and
A.Dolbecq
(2010).
Tetra- to dodecanuclear oxomolybdate complexes with functionalized bisphosphonate ligands: activity in killing tumor cells.
|
| |
Chemistry,
16,
13741-13748.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Gao,
X.Chu,
Y.Qiu,
L.Wu,
Y.Qiao,
J.Wu,
and
D.Li
(2010).
Discovery of potent inhibitor for farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase in the mevalonate pathway.
|
| |
Chem Commun (Camb),
46,
5340-5342.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Jahnke,
J.M.Rondeau,
S.Cotesta,
A.Marzinzik,
X.Pellé,
M.Geiser,
A.Strauss,
M.Götte,
F.Bitsch,
R.Hemmig,
C.Henry,
S.Lehmann,
J.F.Glickman,
T.P.Roddy,
S.J.Stout,
and
J.R.Green
(2010).
Allosteric non-bisphosphonate FPPS inhibitors identified by fragment-based discovery.
|
| |
Nat Chem Biol,
6,
660-666.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Wang,
K.Wang,
Y.L.Liu,
J.H.No,
J.Li,
M.J.Nilges,
and
E.Oldfield
(2010).
Bioorganometallic mechanism of action, and inhibition, of IspH.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
4522-4527.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zhang,
R.Cao,
F.Yin,
F.Y.Lin,
H.Wang,
K.Krysiak,
J.H.No,
D.Mukkamala,
K.Houlihan,
J.Li,
C.T.Morita,
and
E.Oldfield
(2010).
Lipophilic pyridinium bisphosphonates: potent gammadelta T cell stimulators.
|
| |
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,
49,
1136-1138.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Mukherjee,
C.Huang,
F.Guerra,
K.Wang,
and
E.Oldfield
(2009).
Thermodynamics of bisphosphonates binding to human bone: a two-site model.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
131,
8374-8375.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

