 |
PDBsum entry 3duv

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.2.7.7.38
- 3-deoxy-manno-octulosonate cytidylyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
3-deoxy-alpha-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate + CTP = CMP-3-deoxy-beta-D-manno- octulosonate + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
3-deoxy-alpha-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate
|
+
|
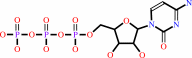 CTP
CTP
|
=
|
CMP-3-deoxy-beta-D-manno- octulosonate
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
64:1292-1294
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of 3-deoxy-manno-octulosonate cytidylyltransferase from Haemophilus influenzae complexed with the substrate 3-deoxy-manno-octulosonate in the beta-configuration.
|
|
H.J.Yoon,
M.J.Ku,
B.Mikami,
S.W.Suh.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The enzyme 3-deoxy-manno-octulosonate cytidylyltransferase (CMP-KDO synthetase;
CKS) catalyzes the activation of 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonate (or
2-keto-3-deoxy-manno-octonic acid; KDO) by forming CMP-KDO. CKS is unique to
Gram-negative bacteria and is an attractive target for the development of
antibacterial agents. The crystal structure of CKS from Haemophilus influenzae
in complex with the substrate KDO has been determined at 2.30 A resolution by
combining single-wavelength anomalous diffraction and molecular-replacement
methods. The two monomers in the asymmetric unit differ in the conformation of
their C-terminal alpha-helix (Ala230-Asn254). The KDO bound to the active site
exists as the beta-pyranose form in the (5)C(2) chair conformation. The
structure of CKS from H. influenzae in complex with KDO will be useful in
structure-based inhibitor design.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1 Structure of H. influenzae CKS bound with the
substrate KDO. (a) Ribbon diagram of the dimer in stereo. Chains
A and B are coloured green and cyan, respectively. The
C-terminal  -helical
region is highlighted in magenta and orange for chains A and B,
respectively, to show the different conformations. These figures
were drawn using the program PyMOL (http://www.pymol.org/ ). (b)
Stereoview of KDO bound to the active site in chain A. The (F[o]
- F[c]) OMIT electron-density map (coloured blue) contoured at
1.0 -helical
region is highlighted in magenta and orange for chains A and B,
respectively, to show the different conformations. These figures
were drawn using the program PyMOL (http://www.pymol.org/ ). (b)
Stereoview of KDO bound to the active site in chain A. The (F[o]
- F[c]) OMIT electron-density map (coloured blue) contoured at
1.0  is
superimposed on the refined model. KDO (red) is shown as a stick
model and the bound water molecules are shown as red balls. The
magenta dotted lines indicate hydrogen bonds. The arrow
indicates the anomeric centre at C2 of KDO. is
superimposed on the refined model. KDO (red) is shown as a stick
model and the bound water molecules are shown as red balls. The
magenta dotted lines indicate hydrogen bonds. The arrow
indicates the anomeric centre at C2 of KDO.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figure is
reprinted
by permission from the IUCr:
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
(2008,
64,
1292-1294)
copyright 2008.
|
|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
H.U.Kim,
T.Y.Kim,
and
S.Y.Lee
(2010).
Genome-scale metabolic network analysis and drug targeting of multi-drug resistant pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii AYE.
|
| |
Mol Biosyst,
6,
339-348.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Cipolla,
L.Gabrielli,
D.Bini,
L.Russo,
and
N.Shaikh
(2010).
Kdo: a critical monosaccharide for bacteria viability.
|
| |
Nat Prod Rep,
27,
1618-1629.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |
|

