 |
PDBsum entry 3drd

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.6.1.105
- lysine--8-amino-7-oxononanoate transaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(8S)-8-amino-7-oxononanoate + L-lysine = (7R,8S)-7,8-diammoniononanoate + (S)-2-amino-6-oxohexanoate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(8S)-8-amino-7-oxononanoate
|
+
|
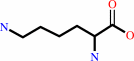 L-lysine
L-lysine
|
=
|
(7R,8S)-7,8-diammoniononanoate
|
+
|
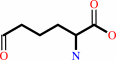 (S)-2-amino-6-oxohexanoate
(S)-2-amino-6-oxohexanoate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
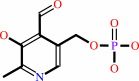 Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
49:6746-6760
(2010)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural characterization of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis biotin biosynthesis enzymes 7,8-diaminopelargonic acid synthase and dethiobiotin synthetase .
|
|
S.Dey,
J.M.Lane,
R.E.Lee,
E.J.Rubin,
J.C.Sacchettini.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) depends on biotin synthesis for survival during
infection. In the absence of biotin, disruption of the biotin biosynthesis
pathway results in cell death rather than growth arrest, an unusual phenotype
for an Mtb auxotroph. Humans lack the enzymes for biotin production, making the
proteins of this essential Mtb pathway promising drug targets. To this end, we
have determined the crystal structures of the second and third enzymes of the
Mtb biotin biosynthetic pathway, 7,8-diaminopelargonic acid synthase (DAPAS) and
dethiobiotin synthetase (DTBS), at respective resolutions of 2.2 A and 1.85 A.
Superimposition of the DAPAS structures bound either to the SAM analog
sinefungin or to 7-keto-8-aminopelargonic acid (KAPA) allowed us to map the
putative binding site for the substrates and to propose a mechanism by which the
enzyme accommodates their disparate structures. Comparison of the DTBS
structures bound to the substrate 7,8-diaminopelargonic acid (DAPA) or to ADP
and the product dethiobiotin (DTB) permitted derivation of an enzyme mechanism.
There are significant differences between the Mtb enzymes and those of other
organisms; the Bacillus subtilis DAPAS, presented here at a high resolution of
2.2 A, has active site variations and the Escherichia coli and Helicobacter
pylori DTBS have alterations in their overall folds. We have begun to exploit
the unique characteristics of the Mtb structures to design specific inhibitors
against the biotin biosynthesis pathway in Mtb.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

