 |
PDBsum entry 3djh

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Isomerase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (mif) at 1.25 a resolution
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Chain: a, b, c. Synonym: mif, phenylpyruvate tautomerase, glycosylation-inhibiting factor, gif. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: mif, glif, mmif. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.25Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.170
|
R-free:
|
0.186
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
G.V.Crichlow,E.Lolis
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
G.V.Crichlow
et al.
(2009).
Structural and kinetic analyses of macrophage migration inhibitory factor active site interactions.
Biochemistry,
48,
132-139.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
23-Jun-08
|
Release date:
|
23-Dec-08
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P14174
(MIF_HUMAN) -
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
115 a.a.
114 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.2.1
- phenylpyruvate tautomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
3-phenylpyruvate = enol-phenylpyruvate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
3-phenylpyruvate
|
=
|
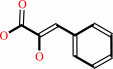 enol-phenylpyruvate
enol-phenylpyruvate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.3.12
- L-dopachrome isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-dopachrome = 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
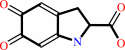 L-dopachrome
L-dopachrome
|
=
|
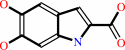 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylate
5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
48:132-139
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural and kinetic analyses of macrophage migration inhibitory factor active site interactions.
|
|
G.V.Crichlow,
J.B.Lubetsky,
L.Leng,
R.Bucala,
E.J.Lolis.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is a secreted protein expressed in
numerous cell types that counters the antiinflammatory effects of
glucocorticoids and has been implicated in sepsis, cancer, and certain
autoimmune diseases. Interestingly, the structure of MIF contains a catalytic
site resembling the tautomerase/isomerase sites of microbial enzymes. While bona
fide physiological substrates remain unknown, model substrates have been
identified. Selected compounds that bind in the tautomerase active site also
inhibit biological functions of MIF. It had previously been shown that the
acetaminophen metabolite, N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI), covalently
binds to the active site of MIF. In this study, kinetic data indicate that NAPQI
inhibits MIF both covalently and noncovalently. The structure of MIF
cocrystallized with NAPQI reveals that the NAPQI has undergone a chemical
alteration forming an acetaminophen dimer (bi-APAP) and binds noncovalently to
MIF at the mouth of the active site. We also find that the commonly used
protease inhibitor, phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF), forms a covalent
complex with MIF and inhibits the tautomerase activity. Crystallographic
analysis reveals the formation of a stable, novel covalent bond for PMSF between
the catalytic nitrogen of the N-terminal proline and the sulfur of PMSF with
complete, well-defined electron density in all three active sites of the MIF
homotrimer. Conclusions are drawn from the structures of these two MIF-inhibitor
complexes regarding the design of novel compounds that may provide more potent
reversible and irreversible inhibition of MIF.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
P.L.Vera,
K.A.Iczkowski,
D.J.Howard,
L.Jiang,
and
K.L.Meyer-Siegler
(2010).
Antagonism of macrophage migration inhibitory factor decreases cyclophosphamide cystitis in mice.
|
| |
Neurourol Urodyn,
29,
1451-1457.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Cho,
G.V.Crichlow,
J.J.Vermeire,
L.Leng,
X.Du,
M.E.Hodsdon,
R.Bucala,
M.Cappello,
M.Gross,
F.Gaeta,
K.Johnson,
and
E.J.Lolis
(2010).
Allosteric inhibition of macrophage migration inhibitory factor revealed by ibudilast.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
11313-11318.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.E.Dobson,
K.D.Augustijn,
J.A.Brannigan,
C.Schnick,
C.J.Janse,
E.J.Dodson,
A.P.Waters,
and
A.J.Wilkinson
(2009).
The crystal structures of macrophage migration inhibitory factor from Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium berghei.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
18,
2578-2591.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

