 |
PDBsum entry 3dfs

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.2.13
- fructose-bisphosphate aldolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate = D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + dihydroxyacetone phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
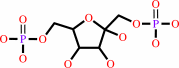 beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
|
=
|
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 90.00% similarity
|
+
|
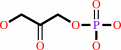 dihydroxyacetone phosphate
dihydroxyacetone phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
48:4528-4537
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Charge stabilization and entropy reduction of central lysine residues in fructose-bisphosphate aldolase.
|
|
M.St-Jean,
C.Blonski,
J.Sygusch.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate muscle aldolase is an essential glycolytic enzyme that
catalyzes reversible carbon-carbon bond formation by cleaving fructose
1,6-bisphosphate to yield dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and d-glyceraldehyde
phosphate. To elucidate the mechanistic role of conserved amino acid Asp-33,
Asn-33 and Ser-33 mutants were examined by kinetic and structural analyses. The
mutations significantly compromised enzymatic activity and carbanion oxidation
in presence of DHAP. Detailed structural analysis demonstrated that, like native
crystals, Asp-33 mutant crystals, soaked in DHAP solutions, trapped Schiff
base-derived intermediates covalently attached to Lys-229. The mutant
structures, however, exhibited an abridged conformational change with the
helical region (34-65) flanking the active site as well as pK(a) reductions and
increased side chain disorder by central lysine residues, Lys-107 and Lys-146.
These changes directly affect their interaction with the C-terminal Tyr-363,
consistent with the absence of active site binding by the C-terminal region in
the presence of phosphate. Lys-146 pK(a) reduction and side chain disorder would
further compromise charge stabilization during C-C bond cleavage and proton
transfer during enamine formation. These mechanistic impediments explain
diminished catalytic activity and a reduced level of carbanion oxidation and are
consistent with rate-determining proton transfer observed in the Asn-33 mutant.
Asp-33 reduces the entropic cost and augments the enthalpic gain during
catalysis by rigidifying Lys-107 and Lys-146, stabilizing their protonated
forms, and promoting a conformational change triggered by substrate or obligate
product binding, which lower kinetic barriers in C-C bond cleavage and Schiff
base-enamine interconversion.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Du,
R.F.Say,
W.Lü,
G.Fuchs,
and
O.Einsle
(2011).
Active-site remodelling in the bifunctional fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase/phosphatase.
|
| |
Nature,
478,
534-537.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

