 |
PDBsum entry 3d8v

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.2.3.1.157
- glucosamine-1-phosphate N-acetyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
alpha-D-glucosamine 1-phosphate + acetyl-CoA = N-acetyl-alpha-D- glucosamine 1-phosphate + CoA + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
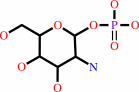 alpha-D-glucosamine 1-phosphate
alpha-D-glucosamine 1-phosphate
|
+
|
 acetyl-CoA
acetyl-CoA
|
=
|
N-acetyl-alpha-D- glucosamine 1-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 50.00% similarity
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.7.23
- UDP-N-acetylglucosamine diphosphorylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine 1-phosphate + UTP + H+ = UDP-N-acetyl- alpha-D-glucosamine + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
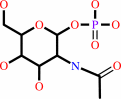 N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine 1-phosphate
N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine 1-phosphate
|
+
|
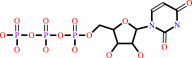 UTP
UTP
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 58.14% similarity
|
=
|
UDP-N-acetyl- alpha-D-glucosamine
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
65:275-283
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure and function of GlmU from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
|
|
Z.Zhang,
E.M.Bulloch,
R.D.Bunker,
E.N.Baker,
C.J.Squire.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Antibiotic resistance is a major issue in the treatment of infectious diseases
such as tuberculosis. Existing antibiotics target only a few cellular pathways
and there is an urgent need for antibiotics that have novel molecular
mechanisms. The glmU gene is essential in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, being
required for optimal bacterial growth, and has been selected as a possible drug
target for structural and functional investigation. GlmU is a bifunctional
acetyltransferase/uridyltransferase that catalyses the formation of UDP-GlcNAc
from GlcN-1-P. UDP-GlcNAc is a substrate for two important biosynthetic
pathways: lipopolysaccharide and peptidoglycan synthesis. The crystal structure
of M. tuberculosis GlmU has been determined in an unliganded form and in complex
with GlcNAc-1-P or UDP-GlcNAc. The structures reveal the residues that are
responsible for substrate binding. Enzyme activities were characterized by (1)H
NMR and suggest that the presence of acetyl-coenzyme A has an inhibitory effect
on uridyltransferase activity.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3 The uridyltransferase active site. (a) Binding of
GlcNAc-1-P (ball-and-stick model). Hydrogen bonds are shown as
dashed lines and the 2F[o] - F[c] electron density is contoured
at 1.0  .
(b) Comparison of GlcNAc-1-P (white outlined protein) and
UDP-GlcNAc (blue protein) binding and associated loop movement
within the uracil site. GlcNAc-1-P and UDP-GlcNAc molecules are
drawn as ball-and-stick models with white- and yellow-coloured C
atoms, respectively. Water molecules are drawn as red spheres
and are associated with the UDP-GlcNAc protein model. .
(b) Comparison of GlcNAc-1-P (white outlined protein) and
UDP-GlcNAc (blue protein) binding and associated loop movement
within the uracil site. GlcNAc-1-P and UDP-GlcNAc molecules are
drawn as ball-and-stick models with white- and yellow-coloured C
atoms, respectively. Water molecules are drawn as red spheres
and are associated with the UDP-GlcNAc protein model.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figure is
reprinted
by permission from the IUCr:
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
(2009,
65,
275-283)
copyright 2009.
|
|
| |
Figure was
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.F.Trempe,
S.Shenker,
G.Kozlov,
and
K.Gehring
(2011).
Self-association studies of the bifunctional N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate uridyltransferase from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
20,
745-752.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.K.Verma,
M.Jaiswal,
N.Kumar,
A.Parikh,
V.K.Nandicoori,
and
B.Prakash
(2009).
Structure of N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate uridyltransferase (GlmU) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a cubic space group.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
65,
435-439.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

