 |
PDBsum entry 3ch6

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3ch6
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
Chains A, B, D, E:
E.C.1.1.1.146
- 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an 11beta-hydroxysteroid + NADP+ = an 11-oxosteroid + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
11beta-hydroxysteroid
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
11-oxosteroid
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, B, D, E:
E.C.1.1.1.201
- 7beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (NADP(+)).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 7beta-hydroxysteroid + NADP+ = a 7-oxosteroid + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
7beta-hydroxysteroid
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 41.94% similarity
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
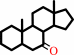 7-oxosteroid
7-oxosteroid
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Bioorg Med Chem Lett
18:3168-3172
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Pyridine amides as potent and selective inhibitors of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1.
|
|
H.Wang,
Z.Ruan,
J.J.Li,
L.M.Simpkins,
R.A.Smirk,
S.C.Wu,
R.D.Hutchins,
D.S.Nirschl,
K.Van Kirk,
C.B.Cooper,
J.C.Sutton,
Z.Ma,
R.Golla,
R.Seethala,
M.E.Salyan,
A.Nayeem,
S.R.Krystek,
S.Sheriff,
D.M.Camac,
P.E.Morin,
B.Carpenter,
J.A.Robl,
R.Zahler,
D.A.Gordon,
L.G.Hamann.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Several series of pyridine amides were identified as selective and potent
11beta-HSD1 inhibitors. The most potent inhibitors feature 2,6- or
3,5-disubstitution on the pyridine core. Various linkers (CH(2)SO(2), CH(2)S,
CH(2)O, S, O, N, bond) between the distal aryl and central pyridyl groups are
tolerated, and lipophilic amide groups are generally favored. On the distal aryl
group, a number of substitutions are well tolerated. A crystal structure was
obtained for a complex between 11beta-HSD1 and the most potent inhibitor in this
series.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

