 |
PDBsum entry 3byc

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.8.2.2
- diisopropyl-fluorophosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
diisopropyl fluorophosphate + H2O = diisopropyl phosphate + fluoride + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 diisopropyl fluorophosphate
diisopropyl fluorophosphate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
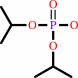 diisopropyl phosphate
diisopropyl phosphate
|
+
|
fluoride
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
106:713-718
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Rapid determination of hydrogen positions and protonation states of diisopropyl fluorophosphatase by joint neutron and X-ray diffraction refinement.
|
|
M.M.Blum,
M.Mustyakimov,
H.Rüterjans,
K.Kehe,
B.P.Schoenborn,
P.Langan,
J.C.Chen.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Hydrogen atoms constitute about half of all atoms in proteins and play a
critical role in enzyme mechanisms and macromolecular and solvent structure.
Hydrogen atom positions can readily be determined by neutron diffraction, and as
such, neutron diffraction is an invaluable tool for elucidating molecular
mechanisms. Joint refinement of neutron and X-ray diffraction data can lead to
improved models compared with the use of neutron data alone and has now been
incorporated into modern, maximum-likelihood based crystallographic refinement
programs like CNS. Joint refinement has been applied to neutron and X-ray
diffraction data collected on crystals of diisopropyl fluorophosphatase
(DFPase), a calcium-dependent phosphotriesterase capable of detoxifying
organophosphorus nerve agents. Neutron omit maps reveal a number of important
features pertaining to the mechanism of DFPase. Solvent molecule W33,
coordinating the catalytic calcium, is a water molecule in a strained
coordination environment, and not a hydroxide. The smallest Ca-O-H angle is 53
degrees , well beyond the smallest angles previously observed. Residue Asp-229,
is deprotonated, supporting a mechanism involving nucleophilic attack by
Asp-229, and excluding water activation by the catalytic calcium. The extended
network of hydrogen bonding interactions in the central water filled tunnel of
DFPase is revealed, showing that internal solvent molecules form an important,
integrated part of the overall structure.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of possible mechanisms for DFPase.
(A) Direct nucleophilic attack of Asp-229 on the substrate, with
a phosphoenzyme intermediate and a fluoride leaving group. (B)
Mechanism involving a calcium-bound hydroxide ion as the active
nucleophile.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of hydrogen bonding interactions in
the central water tunnel of DFPase. Arrows point from H-bond
donor to acceptor. Dashed lines indicate direct metal
coordination. Blue circles represent water molecules, amino
acids are boxed colored according to the propeller blade they
belong to.
|
 |
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
S.Wellert,
B.Tiersch,
J.Koetz,
A.Richardt,
A.Lapp,
O.Holderer,
J.Gäb,
M.M.Blum,
C.Schulreich,
R.Stehle,
and
T.Hellweg
(2011).
The DFPase from Loligo vulgaris in sugar surfactant-based bicontinuous microemulsions: structure, dynamics, and enzyme activity.
|
| |
Eur Biophys J,
40,
761-774.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.S.Gardberg,
A.R.Del Castillo,
K.L.Weiss,
F.Meilleur,
M.P.Blakeley,
and
D.A.Myles
(2010).
Unambiguous determination of H-atom positions: comparing results from neutron and high-resolution X-ray crystallography.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
66,
558-567.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Gäb,
M.Melzer,
K.Kehe,
S.Wellert,
T.Hellweg,
and
M.M.Blum
(2010).
Monitoring the hydrolysis of toxic organophosphonate nerve agents in aqueous buffer and in bicontinuous microemulsions by use of diisopropyl fluorophosphatase (DFPase) with (1)H- (31)P HSQC NMR spectroscopy.
|
| |
Anal Bioanal Chem,
396,
1213-1221.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.M.Blum,
S.J.Tomanicek,
H.John,
B.L.Hanson,
H.Rüterjans,
B.P.Schoenborn,
P.Langan,
and
J.C.Chen
(2010).
X-ray structure of perdeuterated diisopropyl fluorophosphatase (DFPase): perdeuteration of proteins for neutron diffraction.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
66,
379-385.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Z.Fisher,
A.Y.Kovalevsky,
J.F.Domsic,
M.Mustyakimov,
R.McKenna,
D.N.Silverman,
and
P.A.Langan
(2010).
Neutron structure of human carbonic anhydrase II: implications for proton transfer.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
49,
415-421.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.D.Adams,
M.Mustyakimov,
P.V.Afonine,
and
P.Langan
(2009).
Generalized X-ray and neutron crystallographic analysis: more accurate and complete structures for biological macromolecules.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
65,
567-573.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Z.Fisher,
A.Y.Kovalevsky,
J.F.Domsic,
M.Mustyakimov,
D.N.Silverman,
R.McKenna,
and
P.Langan
(2009).
Preliminary joint neutron and X-ray crystallographic study of human carbonic anhydrase II.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
65,
495-498.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

