 |
PDBsum entry 3brm

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of the covalent complex between the bacillus subtilis glutaminase ybgj and 5-oxo-l-norleucine formed by reaction of the protein with 6-diazo-5-oxo-l-norleucine
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Glutaminase 1. Chain: a, b. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Bacillus subtilis. Strain: 168. Gene: glsa1, glsa, ybgj, bsu02430. Expressed in: escherichia coli.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.29Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.178
|
R-free:
|
0.248
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.U.Singer,Y.Kim,I.Dementieva,E.Vinokour,A.Joachimiak,A.Savchenko, A.Yakunin
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
G.Brown
et al.
(2008).
Functional and structural characterization of four glutaminases from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis.
Biochemistry,
47,
5724-5735.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
21-Dec-07
|
Release date:
|
20-May-08
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
O31465
(GLSA1_BACSU) -
Glutaminase 1 from Bacillus subtilis (strain 168)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
327 a.a.
290 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.1.2
- glutaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-glutamine + H2O = L-glutamate + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-glutamine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 81.82% similarity
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
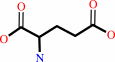 L-glutamate
L-glutamate
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
47:5724-5735
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Functional and structural characterization of four glutaminases from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis.
|
|
G.Brown,
A.Singer,
M.Proudfoot,
T.Skarina,
Y.Kim,
C.Chang,
I.Dementieva,
E.Kuznetsova,
C.F.Gonzalez,
A.Joachimiak,
A.Savchenko,
A.F.Yakunin.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Glutaminases belong to the large superfamily of serine-dependent beta-lactamases
and penicillin-binding proteins, and they catalyze the hydrolytic deamidation of
L-glutamine to L-glutamate. In this work, we purified and biochemically
characterized four predicted glutaminases from Escherichia coli (YbaS and YneH)
and Bacillus subtilis (YlaM and YbgJ). The proteins demonstrated strict
specificity to L-glutamine and did not hydrolyze D-glutamine or L-asparagine. In
each organism, one glutaminase showed higher affinity to glutamine ( E. coli
YbaS and B. subtilis YlaM; K m 7.3 and 7.6 mM, respectively) than the second
glutaminase ( E. coli YneH and B. subtilis YbgJ; K m 27.6 and 30.6 mM,
respectively). The crystal structures of the E. coli YbaS and the B. subtilis
YbgJ revealed the presence of a classical beta-lactamase-like fold and
conservation of several key catalytic residues of beta-lactamases (Ser74, Lys77,
Asn126, Lys268, and Ser269 in YbgJ). Alanine replacement mutagenesis
demonstrated that most of the conserved residues located in the putative
glutaminase catalytic site are essential for activity. The crystal structure of
the YbgJ complex with the glutaminase inhibitor 6-diazo-5-oxo- l-norleucine
revealed the presence of a covalent bond between the inhibitor and the hydroxyl
oxygen of Ser74, providing evidence that Ser74 is the primary catalytic
nucleophile and that the glutaminase reaction proceeds through formation of an
enzyme-glutamyl intermediate. Growth experiments with the E. coli glutaminase
deletion strains revealed that YneH is involved in the assimilation of
l-glutamine as a sole source of carbon and nitrogen and suggested that both
glutaminases (YbaS and YneH) also contribute to acid resistance in E. coli.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.Yoshimune,
Y.Shirakihara,
M.Wakayama,
and
I.Yumoto
(2010).
Crystal structure of salt-tolerant glutaminase from Micrococcus luteus K-3 in the presence and absence of its product L-glutamate and its activator Tris.
|
| |
FEBS J,
277,
738-748.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
U.Grohmann,
and
V.Bronte
(2010).
Control of immune response by amino acid metabolism.
|
| |
Immunol Rev,
236,
243-264.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.S.Bryant,
B.Li,
M.P.Beenhakker,
and
J.R.Huguenard
(2009).
Maintenance of thalamic epileptiform activity depends on the astrocytic glutamate-glutamine cycle.
|
| |
J Neurophysiol,
102,
2880-2888.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.H.Coleman,
and
P.Setlow
(2009).
Analysis of damage due to moist heat treatment of spores of Bacillus subtilis.
|
| |
J Appl Microbiol,
106,
1600-1607.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

