 |
PDBsum entry 3bl7

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Synthetic gene encoded dcps bound to inhibitor dg156844
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Scavenger mRNA-decapping enzyme dcps. Chain: a, b. Fragment: unp residues 38-337. Synonym: dcs-1, hint- related 7megmp-directed hydrolase, histidine triad protein member 5, hint-5. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: dcps, dcs1, hint5. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.31Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.214
|
R-free:
|
0.276
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
B.L.Staker,J.Christensen,L.Stewart,Accelerated Technologies Center For Gene To 3d Structure (Atcg3d)
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.Singh
et al.
(2008).
DcpS as a therapeutic target for spinal muscular atrophy.
Acs Chem Biol,
3,
711-722.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
10-Dec-07
|
Release date:
|
21-Oct-08
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q96C86
(DCPS_HUMAN) -
m7GpppX diphosphatase from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
337 a.a.
286 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.6.1.59
- 5'-(N(7)-methyl 5'-triphosphoguanosine)-[mRNA] diphosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 5'-end (N7-methyl 5'-triphosphoguanosine)-ribonucleoside in mRNA + H2O = N(7)-methyl-GMP + a 5'-end diphospho-ribonucleoside in mRNA + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
M(7)G5'ppp5'N(3'ppp5'N)(n)
|
+
|
H(2)O
|
=
|
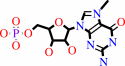 7-methylguanosine 5'-phosphate
7-methylguanosine 5'-phosphate
|
+
|
pp5'N(3'ppp5'N)(n)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
7-methylguanosine 5'-diphosphate
|
+
|
H(2)O
|
=
|
 7-methylguanosine 5'-phosphate
7-methylguanosine 5'-phosphate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Acs Chem Biol
3:711-722
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
DcpS as a therapeutic target for spinal muscular atrophy.
|
|
J.Singh,
M.Salcius,
S.W.Liu,
B.L.Staker,
R.Mishra,
J.Thurmond,
G.Michaud,
D.R.Mattoon,
J.Printen,
J.Christensen,
J.M.Bjornsson,
B.A.Pollok,
M.Kiledjian,
L.Stewart,
J.Jarecki,
M.E.Gurney.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is caused by deletion or mutation of both copies
of the SMN1 gene, which produces an essential protein known as SMN. The severity
of SMA is modified by variable copy number of a second gene,SMN2, which produces
an mRNA that is incorrectly spliced with deletion of the last exon. We described
previously the discovery of potent C5-substituted quinazolines that increase
SMN2 gene expression by 2-fold. Discovery of potent SMN2 promoter inducers
relied on a cellular assay without knowledge of the molecular target. Using
protein microarray scanning with a radiolabeled C5-substituted quinazoline
probe, we identified the scavenger decapping enzyme, DcpS, as a potential
binder. We show that the C5-substituted quinazolines potently inhibit DcpS
decapping activity and that the potency of inhibition correlates with potency
forSMN2 promoter induction. Binding of C5-substituted quinazolines to DcpS holds
the enzyme in an open, catalytically incompetent conformation. DcpS is a nuclear
shuttling protein that binds and hydrolyzes the m(7)GpppN mRNA cap structure and
a modulator of RNA metabolism. Therefore DcpS represents a novel therapeutic
target for modulating gene expression by a small molecule.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Martin,
M.V.St-Pierre,
and
J.F.Dufour
(2011).
Hit proteins, mitochondria and cancer.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1807,
626-632.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.L.Lorson,
H.Rindt,
and
M.Shababi
(2010).
Spinal muscular atrophy: mechanisms and therapeutic strategies.
|
| |
Hum Mol Genet,
19,
R111-R118.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Dimitriadi,
J.N.Sleigh,
A.Walker,
H.C.Chang,
A.Sen,
G.Kalloo,
J.Harris,
T.Barsby,
M.B.Walsh,
J.S.Satterlee,
C.Li,
D.Van Vactor,
S.Artavanis-Tsakonas,
and
A.C.Hart
(2010).
Conserved genes act as modifiers of invertebrate SMN loss of function defects.
|
| |
PLoS Genet,
6,
e1001172.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.E.Butchbach,
J.Singh,
M.Thorsteinsdóttir,
L.Saieva,
E.Slominski,
J.Thurmond,
T.Andrésson,
J.Zhang,
J.D.Edwards,
L.R.Simard,
L.Pellizzoni,
J.Jarecki,
A.H.Burghes,
and
M.E.Gurney
(2010).
Effects of 2,4-diaminoquinazoline derivatives on SMN expression and phenotype in a mouse model for spinal muscular atrophy.
|
| |
Hum Mol Genet,
19,
454-467.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Strenkowska,
J.Kowalska,
M.Lukaszewicz,
J.Zuberek,
W.Su,
R.E.Rhoads,
E.Darzynkiewicz,
and
J.Jemielity
(2010).
Towards mRNA with superior translational activity: synthesis and properties of ARCA tetraphosphates with single phosphorothioate modifications.
|
| |
New J Chem,
34,
993.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.M.Rydzik,
M.Lukaszewicz,
J.Zuberek,
J.Kowalska,
Z.M.Darzynkiewicz,
E.Darzynkiewicz,
and
J.Jemielity
(2009).
Synthetic dinucleotide mRNA cap analogs with tetraphosphate 5',5' bridge containing methylenebis(phosphonate) modification.
|
| |
Org Biomol Chem,
7,
4763-4776.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Farooq,
S.Balabanian,
X.Liu,
M.Holcik,
and
A.MacKenzie
(2009).
p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase stabilizes SMN mRNA through RNA binding protein HuR.
|
| |
Hum Mol Genet,
18,
4035-4045.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

