 |
PDBsum entry 3zh4
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.7
- UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 1-carboxyvinyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Peptidoglycan Biosynthesis (Part 1)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
phosphoenolpyruvate + UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine = UDP-N-acetyl-3- O-(1-carboxyvinyl)-alpha-D-glucosamine + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
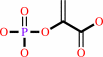 phosphoenolpyruvate
phosphoenolpyruvate
|
+
|
UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine
|
=
|
UDP-N-acetyl-3- O-(1-carboxyvinyl)-alpha-D-glucosamine
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Antimicrob Agents Chemother
57:2801-2808
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Heteroresistance to fosfomycin is predominant in Streptococcus pneumoniae and depends on the murA1 gene.
|
|
H.Engel,
J.Gutiérrez-Fernández,
C.Flückiger,
M.Martínez-Ripoll,
K.Mühlemann,
J.A.Hermoso,
M.Hilty,
L.J.Hathaway.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Fosfomycin targets the first step of peptidoglycan biosynthesis in Streptococcus
pneumoniae catalyzed by UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyltransferase (MurA1).
We investigated whether heteroresistance to fosfomycin occurs in S. pneumoniae.
We found that of 11 strains tested, all but 1 (Hungary(19A)) displayed
heteroresistance and that deletion of murA1 abolished heteroresistance.
Hungary(19A) differs from the other strains by a single amino acid substitution
in MurA1 (Ala364Thr). To test whether this substitution is responsible for the
lack of heteroresistance, it was introduced into strain D39. The
heteroresistance phenotype of strain D39 was not changed. Furthermore, no
relevant structural differences between the MurA1 crystal structures of
heteroresistant strain D39 and nonheteroresistant strain Hungary(19A) were
found. Our results reveal that heteroresistance to fosfomycin is the predominant
phenotype of S. pneumoniae and that MurA1 is required for heteroresistance to
fosfomycin but is not the only factor involved. The findings provide a caveat
for any future use of fosfomycin in the treatment of pneumococcal infections.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

