 |
PDBsum entry 3w7b
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of formyltetrahydrofolate deformylase from thermus thermophilus hb8
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Formyltetrahydrofolate deformylase. Chain: a, b. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Thermus thermophilus. Organism_taxid: 300852. Strain: hb8 / atcc 27634 / dsm 579. Gene: ttha1321. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.71Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.208
|
R-free:
|
0.261
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
G.Sampei,Y.Yanagida,N.Ogata,M.Kusano,K.Terao,H.Kawai,Y.Fukai, M.Kanagawa,Y.Inoue,S.Baba,G.Kawai
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
G.Sampei
et al.
(2013).
Structures and reaction mechanisms of the two related enzymes, PurN and PurU.
J Biochem (tokyo),
154,
569-579.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
28-Feb-13
|
Release date:
|
08-Jan-14
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q5SIP8
(Q5SIP8_THET8) -
Formyltetrahydrofolate deformylase from Thermus thermophilus (strain ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / HB8)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
285 a.a.
285 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.1.10
- formyltetrahydrofolate deformylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Folate Coenzymes
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(6R)-10-formyltetrahydrofolate + H2O = (6S)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate + formate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(6R)-10-formyltetrahydrofolate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
(6S)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate
|
+
|
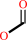 formate
formate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biochem (tokyo)
154:569-579
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structures and reaction mechanisms of the two related enzymes, PurN and PurU.
|
|
G.Sampei,
M.Kanagawa,
S.Baba,
T.Shimasaki,
H.Taka,
S.Mitsui,
S.Fujiwara,
Y.Yanagida,
M.Kusano,
S.Suzuki,
K.Terao,
H.Kawai,
Y.Fukai,
N.Nakagawa,
A.Ebihara,
S.Kuramitsu,
S.Yokoyama,
G.Kawai.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The crystal structures of glycinamide ribonucleotide transformylases (PurNs)
from Aquifex aeolicus (Aa), Geobacillus kaustophilus (Gk) and Symbiobacterium
toebii (St), and of formyltetrahydrofolate hydrolase (PurU) from Thermus
thermophilus (Tt) were determined. The monomer structures of the determined PurN
and PurU were very similar to the known structure of PurN, but oligomeric states
were different; AaPurN and StPurN formed dimers, GkPurN formed monomer and PurU
formed tetramer in the crystals. PurU had a regulatory ACT domain in its
N-terminal side. So far several structures of PurUs have been determined, yet,
the mechanisms of the catalysis and the regulation of PurU have not been
elucidated. We, therefore, modelled ligand-bound structures of PurN and PurU,
and performed molecular dynamics simulations to elucidate the reaction
mechanisms. The evolutionary relationship of the two enzymes is discussed based
on the comparisons of the structures and the catalytic mechanisms.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

