 |
PDBsum entry 3vjc

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Transferase/transferase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3vjc
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase/transferase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of the human squalene synthase in complex with zaragozic acid a
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Squalene synthase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f. Fragment: unp residues 31-370. Synonym: sqs, ss, fpp:fpp farnesyltransferase, farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: fdft1. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.89Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.150
|
R-free:
|
0.197
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
C.I.Liu,W.Y.Jeng,W.J.Chang,T.P.Ko,A.H.J.Wang
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
C.I.Liu
et al.
(2012).
Binding modes of zaragozic acid A to human squalene synthase and staphylococcal dehydrosqualene synthase.
J Biol Chem,
287,
18750-18757.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
14-Oct-11
|
Release date:
|
11-Apr-12
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P37268
(FDFT_HUMAN) -
Squalene synthase from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
417 a.a.
334 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.21
- squalene synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Squalene and Phytoene Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
2 (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate + NADPH + H+ = squalene + 2 diphosphate + NADP+
|
|
2.
|
2 (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate + NADH + H+ = squalene + 2 diphosphate + NAD+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
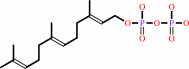 2
×
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
2
×
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
squalene
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 55.56% similarity
|
+
|
 2
×
diphosphate
2
×
diphosphate
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 2
×
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
2
×
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
squalene
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 55.56% similarity
|
+
|
 2
×
diphosphate
2
×
diphosphate
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mn(2+) or Mg(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Biol Chem
287:18750-18757
(2012)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Binding modes of zaragozic acid A to human squalene synthase and staphylococcal dehydrosqualene synthase.
|
|
C.I.Liu,
W.Y.Jeng,
W.J.Chang,
T.P.Ko,
A.H.Wang.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Zaragozic acids (ZAs) belong to a family of fungal metabolites with nanomolar
inhibitory activity toward squalene synthase (SQS). The enzyme catalyzes the
committed step of sterol synthesis and has attracted attention as a potential
target for antilipogenic and antiinfective therapies. Here, we have determined
the structure of ZA-A complexed with human SQS. ZA-A binding induces a local
conformational change in the substrate binding site, and its C-6 acyl group also
extends over to the cofactor binding cavity. In addition, ZA-A effectively
inhibits a homologous bacterial enzyme, dehydrosqualene synthase (CrtM), which
synthesizes the precursor of staphyloxanthin in Staphylococcus aureus to cope
with oxidative stress. Size reduction at Tyr(248) in CrtM further increases the
ZA-A binding affinity, and it reveals a similar overall inhibitor binding mode
to that of human SQS/ZA-A except for the C-6 acyl group. These structures pave
the way for further improving selectivity and development of a new generation of
anticholesterolemic and antimicrobial inhibitors.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

