 |
PDBsum entry 3qa2

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Transferase/transferase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3qa2
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.1.3
- ketohexokinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
beta-D-fructose + ATP = beta-D-fructose 1-phosphate + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
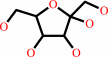 beta-D-fructose
beta-D-fructose
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
beta-D-fructose 1-phosphate
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acs Med Chem Lett
2:538-543
(2011)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Inhibitors of Ketohexokinase: Discovery of Pyrimidinopyrimidines with Specific Substitution that Complements the ATP-Binding Site.
|
|
B.E.Maryanoff,
J.C.O'Neill,
D.F.McComsey,
S.C.Yabut,
D.K.Luci,
A.D.Jordan,
J.A.Masucci,
W.J.Jones,
M.C.Abad,
A.C.Gibbs,
I.Petrounia.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Attenuation of fructose metabolism by the inhibition of ketohexokinase (KHK;
fructokinase) should reduce body weight, free fatty acids, and triglycerides,
thereby offering a novel approach to treat diabetes and obesity in response to
modern diets. We have identified potent, selective inhibitors of human hepatic
KHK within a series of pyrimidinopyrimidines (1). For example, 8, 38, and 47
exhibited KHK IC50 values of 12, 7, and 8 nM, respectively, and also showed
potent cellular KHK inhibition (IC50 < 500 nM), which relates to their
intrinsic potency vs KHK and their ability to penetrate cells. X-ray cocrystal
structures of KHK complexes of 3, 8, and 47 revealed the important interactions
within the enzyme's adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP)-binding pocket.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

