 |
PDBsum entry 3pvr

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3pvr
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 304 a.a.
304 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 236 a.a.
236 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 248 a.a.
248 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
The phenylacetyl-coa monooxygenase paaac subcomplex with benzoyl-coa
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Phenylacetic acid degradation protein paaa. Chain: a. Synonym: phenylacetyl-coa ring 1,2-epoxidase paaa. Engineered: yes. Phenylacetic acid degradation protein paac. Chain: b, c. Synonym: phenylacetyl-coa ring 1,2-epoxidase paac. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 511145. Strain: k12 substr. Mg1655. Gene: b1388, jw1383, paaa, ydbo. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008. Gene: b1390, jw1385, paac, ydbp.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.10Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.190
|
R-free:
|
0.225
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.Cygler,A.M.Grishin,Montreal-Kingston Bacterial Structural Genomics Initiative (Bsgi)
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
A.M.Grishin
et al.
(2011).
Structural and functional studies of the Escherichia coli phenylacetyl-CoA monooxygenase complex.
J Biol Chem,
286,
10735-10743.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
07-Dec-10
|
Release date:
|
19-Jan-11
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P76077
(PAAA_ECOLI) -
1,2-phenylacetyl-CoA epoxidase, subunit A from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
309 a.a.
304 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chain A:
E.C.1.14.13.149
- phenylacetyl-CoA 1,2-epoxidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
phenylacetyl-CoA + NADPH + O2 + H+ = 2-(1,2-epoxy-1,2- dihydrophenyl)acetyl-CoA + NADP+ + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
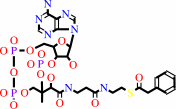 phenylacetyl-CoA
phenylacetyl-CoA
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 98.25% similarity
|
=
|
2-(1,2-epoxy-1,2- dihydrophenyl)acetyl-CoA
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
286:10735-10743
(2011)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural and functional studies of the Escherichia coli phenylacetyl-CoA monooxygenase complex.
|
|
A.M.Grishin,
E.Ajamian,
L.Tao,
L.Zhang,
R.Menard,
M.Cygler.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The utilization of phenylacetic acid (PA) in Escherichia coli occurs through a
hybrid pathway that shows features of both aerobic and anaerobic metabolism.
Oxygenation of the aromatic ring is performed by a multisubunit
phenylacetyl-coenzyme A oxygenase complex that shares remote homology of two
subunits to well studied bacterial multicomponent monooxygenases and was
postulated to form a new bacterial multicomponent monooxygenase subfamily. We
expressed the subunits PaaA, B, C, D, and E of the PA-CoA oxygenase and showed
that PaaABC, PaaAC, and PaaBC form stable subcomplexes that can be purified. In
vitro reconstitution of the oxygenase subunits showed that each of the PaaA, B,
C, and E subunits are necessary for catalysis, whereas PaaD is not essential. We
have determined the crystal structure of the PaaAC complex in a ligand-free form
and with several CoA derivatives. We conclude that PaaAC forms a catalytic core
with a monooxygenase fold with PaaA being the catalytic α subunit and PaaC, the
structural β subunit. PaaAC forms heterotetramers that are organized very
differently from other known multisubunit monooxygenases and lacks their
conservative network of hydrogen bonds between the di-iron center and protein
surface, suggesting different association with the reductase and different
mechanisms of electron transport. The PaaA structure shows adaptation of the
common access route to the active site for binding a CoA-bound substrate. The
enzyme-substrate complex shows the orientation of the aromatic ring, which is
poised for oxygenation at the ortho-position, in accordance with the expected
chemistry. The PA-CoA oxygenase complex serves as a paradigm for the new
subfamily multicomponent monooxygenases comprising several hundred homologs.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
R.Teufel,
T.Friedrich,
and
G.Fuchs
(2012).
An oxygenase that forms and deoxygenates toxic epoxide.
|
| |
Nature,
483,
359-362.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |
| |

