 |
PDBsum entry 3n5e

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Transferase/transferase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3n5e
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase/transferase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of human thymidylate synthase bound to a peptide inhibitor
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Thymidylate synthase. Chain: a. Synonym: tsase, ts. Engineered: yes. Thymidylate synthase. Chain: b. Synonym: tsase, ts. Engineered: yes. Synthetic peptide lr.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: tyms, ts, ok/sw-cl.29. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Synthetic: yes. Other_details: synthetic peptide (8mer)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.26Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.189
|
R-free:
|
0.221
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
C.Pozzi,D.Cardinale,G.Guaitoli,D.Tondi,R.Luciani,H.Myllykallio, S.Ferrari,M.P.Costi,S.Mangani
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
D.Cardinale
et al.
(2011).
Protein-protein interface-binding peptides inhibit the cancer therapy target human thymidylate synthase.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
108,
E542.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
25-May-10
|
Release date:
|
08-Jun-11
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P04818
(TYSY_HUMAN) -
Thymidylate synthase from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
313 a.a.
263 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 3 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.1.1.45
- thymidylate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Folate Coenzymes
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
dUMP + (6R)-5,10-methylene-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate = 7,8-dihydrofolate + dTMP
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
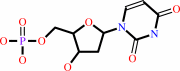 dUMP
dUMP
|
+
|
(6R)-5,10-methylene-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 40.91% similarity
|
=
|
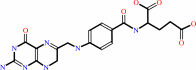 7,8-dihydrofolate
7,8-dihydrofolate
|
+
|
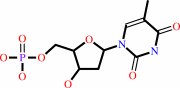 dTMP
dTMP
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
108:E542
(2011)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Protein-protein interface-binding peptides inhibit the cancer therapy target human thymidylate synthase.
|
|
D.Cardinale,
G.Guaitoli,
D.Tondi,
R.Luciani,
S.Henrich,
O.M.Salo-Ahen,
S.Ferrari,
G.Marverti,
D.Guerrieri,
A.Ligabue,
C.Frassineti,
C.Pozzi,
S.Mangani,
D.Fessas,
R.Guerrini,
G.Ponterini,
R.C.Wade,
M.P.Costi.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Human thymidylate synthase is a homodimeric enzyme that plays a key role in DNA
synthesis and is a target for several clinically important anticancer drugs that
bind to its active site. We have designed peptides to specifically target its
dimer interface. Here we show through X-ray diffraction, spectroscopic, kinetic,
and calorimetric evidence that the peptides do indeed bind at the interface of
the dimeric protein and stabilize its di-inactive form. The "LR"
peptide binds at a previously unknown binding site and shows a previously
undescribed mechanism for the allosteric inhibition of a homodimeric enzyme. It
inhibits the intracellular enzyme in ovarian cancer cells and reduces cellular
growth at low micromolar concentrations in both cisplatin-sensitive and
-resistant cells without causing protein overexpression. This peptide
demonstrates the potential of allosteric inhibition of hTS for overcoming
platinum drug resistance in ovarian cancer.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

